The Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 34136558
- PMCID: PMC8200483
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2021.683886
The Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells
Abstract
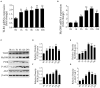
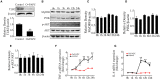
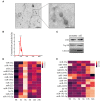
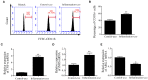
Mastitis, an inflammatory disease, causes severe economic loss in the dairy industry, which is mainly infected by bacteria. Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), the major pathogenic microorganism, derived from lipoteichoic acid (LTA) has been identified to activate inflammatory responses, but the cellular or intercellular regulatory mechanism is unclear. This study mainly focused on the effects of LTA in bovine mammary epithelial cells (Mac-T) and elaborated the regulation of microRNAs (miRNAs). The results showed that LTA enhanced the messenger RNA (mRNA) expression and production of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and interleukin (IL)-6. Furthermore, LTA could activate Toll-like receptor (TLR)2/MyD88-mediated phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway, and TLR2 plays a pivotal role in LTA-induced inflammatory responses. The results of qRT-PCR showed that miRNA levels increased and reached the highest at 3 h and then gradually decreased over time in Mac-T cells. In exosomes, the levels of 11 and three miRNAs were upregulated and downregulated at 24 h, respectively. In addition, miR-23a showed the highest increase in Mac-T cells treated with LTA and targeted PI3K to regulate inflammatory responses. Furthermore, Mac-T cell-derived exosomes were identified to play a cell-cell communication by promoting M1 polarization of bovine macrophages. In summary, our study demonstrated that LTA could activate inflammatory responses via TLR2/MyD88/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, and miR-23a inhibited it by targeting PI3K. Furthermore, we found that Mac-T cell-derived exosomes might be associated with inflammatory responses by promoting M1 polarization of bovine macrophages.
Keywords: LTA; exosome; mammary epithelial cells; mastitis; miR-23a.
Copyright © 2021 Cai, Fan, Li, Sun, Dai, Lei, Dai and Liao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Valckenier D, Piepers S, De Visscher A, Bruckmaier RM, De Vliegher S. Effect of intramammary infection with non-aureus staphylococci in early lactation in dairy heifers on quarter somatic cell count and quarter milk yield during the first 4 months of lactation. J Dairy Sci. (2019) 102:6442–53. 10.3168/jds.2018-15913 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

