Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000511 Improves Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition of Cervical Cancer by Regulating hsa-mir-296-5p/HMGA1
- PMID: 34136582
- PMCID: PMC8175136
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9964538
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000511 Improves Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition of Cervical Cancer by Regulating hsa-mir-296-5p/HMGA1
Abstract
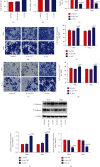
As the second largest gynecological cancer, cervical cancer has been widely reported in recent years in which circular RNA is involved in the disease process. We earlier found that the expression of hsa_circ_0000511 in cervical cancer cells increased significantly, but its role in the process of cervical cancer is not clear. The purpose of this study is to explore its possible mechanisms in cervical cancer. Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), cell counting kit-8 assay, Transwell test, cell transfection, RNA pull-down assay and dual-luciferase reporter assay, and Western blot analysis were used to detect the expression and distribution of hsa_circ_0000511 in SiHa and HeLa cells, the ability of invasion and proliferation, and the modulated relationships between hsa_circ_0000511 and hsa-mir-296-5p, hsa-mir-296-5p, and HMGA1. hsa_circ_0000511 had the highest expression in SiHa and HeLa cells, and the expression in the cytoplasm was significantly higher than that in the nucleus, and its expression was not affected by RNase R. When hsa_circ_0000511 was silenced, its expression in SiHa and HeLa cells was significantly decreased; the proliferation, invasion, and migration abilities of the two kinds of cells were significantly enhanced; and the protein expression of E-cadherin was significantly upregulated, while the protein expression of N-cadherin was significantly downregulated. The expression of hsa-mir-296-5p was lower in SiHa and HeLa cells; however, its expression was increased when hsa_circ_0000511 was inhibited and decreased when hsa_circ_0000511 was overexpressed, so did the ability of proliferation, invasion, and migration and the protein expression of E-cadherin. Interestingly, the protein expression of HMGA1 also changed in these two cells when hsa-mir-296-5p was inhibited or overexpressed. Our results indicate that the upregulated hsa_circ_0000511 can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and migration of SiHa and HeLa cells by regulating hsa-mir-296-5p/HMGA1, suggesting that the hsa_circ_0000511/hsa-mir-296-5p/HMGA1 pathway may be a potential target for the treatment of cervical cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Jia Xie et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

