Removal of Cu (II) by calcinated electroplating sludge
- PMID: 34136684
- PMCID: PMC8176314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07092
Removal of Cu (II) by calcinated electroplating sludge
Abstract
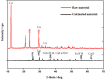
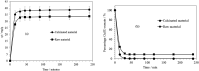
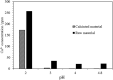
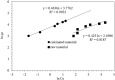
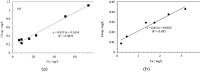
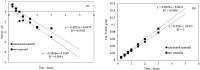
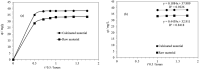
Electroplating sludge consists of various heavy metal oxides, which may be utilized as adsorbent to remove Cu (II) present in aqueous environment. This study evaluated the adsorption performance of calcinated electroplating sludge. The adsorption isotherm based on Langmuir equation proved that calcinated electroplating sludge had a higher adsorption performance than raw electroplating sludge, with maximum adsorption capacity 92 mg/g and 76.34 mg/g, respectively. Findings of the conducted kinetic study revealed that both surface adsorption and intra-particular diffusion were involved during the adsorption process. Moreover, the comparison between the experimental and calculated data of equilibrium adsorption capacity demonstrated that the pseudo second-order kinetic equation fitted well with 38.31 mg/g of calcinated sludge and 33.66 mg/g of raw sludge, approximate to real-world data. Furthermore, adsorption mechanism research demonstrated that while OH group plays a vital role in raw sample, Ca2+, in addition to OH group, was involved in ion exchange in calcinated sample.
Keywords: Adsorption; Adsorption isotherm; Calcinated electroplating sludge; Cu (II) removal; Kinetic study; Raw electroplating sludge.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abdelkader L., Asier M.S., Susana C.M.F., Jalel L., Manef A. Adsorption of copper on chitin-based materials: kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016:1–9. 000.
-
- Al-Degs Y.S., El-Barghouthi M.I., Issa A.A., Khraisheh M.A., Walker G.M. Sorption of Zn(II), Pb(II), and Co(II) using natural sorbents. Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Water Res. 2006;40:2645–2658. - PubMed
-
- Asiabi H., Yamini Y., Shamsayei M., Tahmasebi E. Highly selective and efficient removal and extraction of heavy metals by layered double hydroxides intercalated with the diphenylamine-4-sulfonate. a comparative study. Chem. Eng. J. 2017;323:212–223.
-
- Awual M.R. New type mesoporous conjugate material for selective optical copper(II) ions monitoring & removal from polluted waters. Chem. Eng. J. 2017;307:85–94.
-
- Bhattacharyya D., Jumawan A.B., Jr., Grieves R.B. Separation of toxic heavy metals by sulfide precipitation. Separ. Sci. Technol. 1979;14:441–452.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

