Development, Acceptance, and Concerns Surrounding App-Based Services to Overcome the COVID-19 Outbreak in South Korea: Web-Based Survey Study
- PMID: 34137726
- PMCID: PMC8330629
- DOI: 10.2196/29315
Development, Acceptance, and Concerns Surrounding App-Based Services to Overcome the COVID-19 Outbreak in South Korea: Web-Based Survey Study
Abstract
Background: Since the COVID-19 outbreak, South Korea has been engaged in various efforts to overcome the pandemic. One of them is to provide app-based COVID-19-related services to the public. As the pandemic continues, a need for various apps has emerged, including COVID-19 apps that can support activities aimed at overcoming the COVID-19 pandemic.
Objective: We aimed to determine which apps were considered the most necessary according to users and evaluate the current status of the development of COVID-19-related apps in South Korea. We also aimed to determine users' acceptance and concerns related to using apps to support activities to combat COVID-19.
Methods: We collected data from 1148 users from a web-based survey conducted between November 11 and December 6, 2020. Basic statistical analysis, multiple response analysis, and the Wilcoxon rank sum test were performed using R software. We then manually classified the current status of the development of COVID-19-related apps.
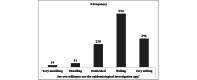
Results: In total, 68.4% (785/1148) of the respondents showed high willingness to protect themselves from COVID-19 by using related apps. Users considered the epidemiological investigation app to be the most necessary app (709/1148, 61.8%) overall, followed by the self-management app for self-isolation (613/1148, 53.4%), self-route management app (605/1148, 52.7%), COVID-19 symptom management app (483/1148, 42.1%), COVID-19-related information provision app (339/1148, 29.5%), and mental health management app (270/1148, 23.5%). Despite the high intention to use these apps, users were also concerned about privacy issues and media exposure. Those who had an underlying disease and had experience using COVID-19-related apps showed significantly higher intentions to use those apps (P=.05 and P=.01, respectively).
Conclusions: Targeting users is very important in order to design and develop the most necessary apps. Furthermore, to gain the public's trust and make the apps available to as many people as possible, it is vital to develop diverse apps in which privacy protection is maximized.
Keywords: COVID-19; acceptance; app-based services; concerns; epidemiological investigation, self-route management app, privacy.
©Jihwan Park, Jinhyun Han, Yerin Kim, Mi Jung Rho. Originally published in JMIR Medical Informatics (https://medinform.jmir.org), 30.07.2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The corresponding author (MJR) and the first author (JP) are a married couple. There are no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lee D, Lee J. Testing on the move: South Korea's rapid response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect. 2020 May;5:100111. doi: 10.1016/j.trip.2020.100111. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2590-1982(20)30022-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abeler J, Bäcker M, Buermeyer U, Zillessen H. COVID-19 contact tracing and data protection can go together. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Apr 20;8(4):e19359. doi: 10.2196/19359. https://mhealth.jmir.org/2020/4/e19359/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang S, Ding S, Xiong L. A new system for surveillance and digital contact tracing for COVID-19: spatiotemporal reporting over network and GPS. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Jun 10;8(6):e19457. doi: 10.2196/19457. https://mhealth.jmir.org/2020/6/e19457/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jonker M, de Bekker-Grob E, Veldwijk J, Goossens L, Bour S, Rutten-Van Mölken M. COVID-19 contact tracing apps: predicted uptake in the Netherlands based on a discrete choice experiment. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Oct 09;8(10):e20741. doi: 10.2196/20741. https://mhealth.jmir.org/2020/10/e20741/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials