Brain death and management of the potential donor
- PMID: 34138388
- PMCID: PMC8210518
- DOI: 10.1007/s10072-021-05360-6
Brain death and management of the potential donor
Abstract
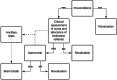
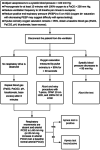
One of the first attempts to define brain death (BD) dates from 1963, and since then, the diagnosis criteria of that entity have evolved. In spite of the publication of practice parameters and evidence-based guidelines, BD is still causing concern and controversies in the society. The difficulties in determining brain death and making it understood by family members not only endorse futile therapies and increase health care costs, but also hinder the organ transplantation process. This review aims to give an overview about the definition of BD, causes, physiopathology, diagnosis criteria, and management of the potential brain-dead donor. It is important to note that the BD determination criteria detailed here follow the AAN's recommendations, but the standard practice for BD diagnosis varies from one country to another.
Keywords: Brain death; Critical care; Diagnosis; Management; Organ donation.
© 2021. Fondazione Società Italiana di Neurologia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Beck CS, Pritchard WH, Feil HS. Ventricular fibrillation of long duration abolished by electric shock. J Am Med Assoc. 1947;135(15):985. - PubMed
-
- Bower AG, Bennett VR, Dillon JB, Axelrod B. Investigation on the care and treatment of poliomyelitis patients. Ann West Med Surg. 1950;4(10):561–582. - PubMed
-
- Puri N, Puri V, Dellinger RP. History of technology in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Clin. 2009;25(1):185–200. - PubMed
-
- Schwab RS, Potts F, Bonazzi A. EEG as an aid to determining death in the presence of cardiac activity (ethical, legal and medical aspects) Electroenceph Clin Neurophyslol. 1963;15:145–166.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

