Comparison of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and prognostic nutritional index with other clinical and molecular biomarkers for prediction of glioblastoma multiforme outcome
- PMID: 34138894
- PMCID: PMC8211244
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252614
Comparison of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and prognostic nutritional index with other clinical and molecular biomarkers for prediction of glioblastoma multiforme outcome
Abstract
Objective: Pre- and post-operative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) and other prognostic clinicopathological variables were correlated with progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) patients.
Methods: GBM patients (n = 87, single-centre, recruited 2013-2019) were retrospectively divided into low and high groups using literature-derived cut-offs (NLR = 5.07, PNI = 46.97). Kaplan-Meier survival curves and log rank tests assessed PFS and OS. Univariate and multivariate analyses identified PFS and OS prognosticators.
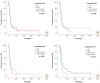
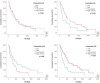
Results: High vs low post-operative PNI cohort was associated with longer PFS (279 vs 136 days, p = 0.009), but significance was lost on multivariate analysis. Post-operative ECOG (p = 0.043), daily dexamethasone (p = 0.023) and IDH mutation (p = 0.046) were significant on multivariate analysis for PFS. High pre- and post-operative PNI were associated with improved OS (384 vs 114 days, p = 0.034 and 516 vs 245 days, p = 0.001, respectively). Low postoperative NLR correlated with OS (408 vs 249 days, p = 0.029). On multivariate analysis using forward selection process, extent of resection (EOR) (GTR vs biopsy, p = 0.004 and STR vs biopsy, p = 0.011), and any previous surgery (p = 0.014) were independent prognostic biomarkers for OS. On multivariate analysis of these latter variables with literature-derived prognostic biomarkers, EOR remained significantly associated with OS (p = 0.037).
Conclusions: EOR, followed by having any surgery prior to GBM, are the most significant independent predictors of GBM patient's OS. Post-operative ECOG, daily dexamethasone and IDH mutation are independent prognostic biomarkers for PFS. PNI may be superior to NLR. Post- vs pre-operative serum inflammatory marker levels may be associated with survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pre-operative hematological markers as predictive factors for overall survival and progression free survival in glioblastomas.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Oct;197:106162. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106162. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32890893
-
Clinical significance of postoperatif controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score in glioblastoma multiforme.J Clin Neurosci. 2021 Apr;86:260-266. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2021.01.036. Epub 2021 Feb 19. J Clin Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33775339
-
The prognostic value of prognostic nutritional index (PNI) and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) for advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with platinum-based chemotherapeutics.Ann Palliat Med. 2020 May;9(3):967-978. doi: 10.21037/apm.2020.04.31. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Ann Palliat Med. 2020. PMID: 32389020
-
Prognostic Significance of Preoperative Systemic Cellular Inflammatory Markers in Gliomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Clin Transl Sci. 2020 Jan;13(1):179-188. doi: 10.1111/cts.12700. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Clin Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 31550075 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of IDH 1 mutation in patients with glioblastoma multiforme.J Pak Med Assoc. 2017 May;67(5):816-817. J Pak Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28507382 Review.
Cited by
-
Dexamethasone in Patients with Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 1;16(7):1393. doi: 10.3390/cancers16071393. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of prognostic nutritional index score and controlling nutritional status score in patients with glioblastoma: A comprehensive meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 16;13:1117764. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1117764. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36874094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Values of Systemic Inflammatory Immunological Markers in Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 25;15(13):3339. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133339. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Simple Preoperative Blood Count to Stratify Prognosis in Isocitrate Dehydrogenase-Wildtype Glioblastoma Patients Treated with Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 18;13(22):5778. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225778. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830935 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic and local immunosuppression in glioblastoma and its prognostic significance.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 28;15:1326753. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1326753. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38481999 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brenner A, Friger M, Geffen DB, et al.. The Prognostic Value of the Pretreatment Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Glioblastoma Multiforme Brain Tumors: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Patients Treated with Combined Modality Surgery, Radiation Therapy, and Temozolomide Chemotherapy. Oncology. 2019;97(5):255–63. 10.1159/000500926 - DOI - PubMed
-
- McNamara MG, Lwin Z, Jiang H, et al.. Factors impacting survival following second surgery in patients with glioblastoma in the temozolomide treatment era, incorporating neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and time to first progression. J Neurooncol. 2014;117(1):147–52. 10.1007/s11060-014-1366-9 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

