A time-resolved proteomic and prognostic map of COVID-19
- PMID: 34139154
- PMCID: PMC8201874
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cels.2021.05.005
A time-resolved proteomic and prognostic map of COVID-19
Abstract
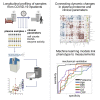
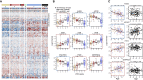
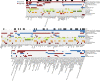
COVID-19 is highly variable in its clinical presentation, ranging from asymptomatic infection to severe organ damage and death. We characterized the time-dependent progression of the disease in 139 COVID-19 inpatients by measuring 86 accredited diagnostic parameters, such as blood cell counts and enzyme activities, as well as untargeted plasma proteomes at 687 sampling points. We report an initial spike in a systemic inflammatory response, which is gradually alleviated and followed by a protein signature indicative of tissue repair, metabolic reconstitution, and immunomodulation. We identify prognostic marker signatures for devising risk-adapted treatment strategies and use machine learning to classify therapeutic needs. We show that the machine learning models based on the proteome are transferable to an independent cohort. Our study presents a map linking routinely used clinical diagnostic parameters to plasma proteomes and their dynamics in an infectious disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; biomarkers; clinical disease progression; disease prognosis; longitudinal profiling; machine learning; patient trajectories; physiological parameters; proteomics.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Aĝirbaşli M., Song J., Lei F., Wang S., Kunselman A.R., Clark J.B., Myers J.L., Ündar A. Apolipoprotein E levels in pediatric patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. Artif. Organs. 2015;39:28–33. - PubMed
-
- Anderson N.L., Anderson N.G. The human plasma proteome: history, character, and diagnostic prospects. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2002;1:845–867. - PubMed
-
- ARDS Definition Task Force, Ranieri V.M., Rubenfeld G.D., Thompson B.T., Ferguson N.D., Caldwell E., Fan E., Camporota L., Slutsky A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition. JAMA. 2012;307:2526–2533. - PubMed
-
- Banda M.J., Rice A.G., Griffin G.L., Senior R.M. Alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor is a neutrophil chemoattractant after proteolytic inactivation by macrophage elastase. J. Biol. Chem. 1988;263:4481–4484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

