Coronavirus disease 2019 in heart transplant recipients: Risk factors, immunosuppression, and outcomes
- PMID: 34140222
- PMCID: PMC8131557
- DOI: 10.1016/j.healun.2021.05.006
Coronavirus disease 2019 in heart transplant recipients: Risk factors, immunosuppression, and outcomes
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 continues to inflict significant morbidity and mortality, particularly on patients with preexisting health conditions. The clinical course, outcomes, and significance of immunosuppression regimen in heart transplant recipients with COVID-19 remains unclear.
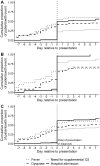
Methods: We included the first 99 heart transplant recipients at participating centers with COVID-19 and followed patients until resolution. We collected baseline information, symptoms, laboratory studies, vital signs, and outcomes for included patients. The association of immunosuppression regimens at baseline with severe disease were compared using logistic regression, adjusting for age and time since transplant.
Results: The median age was 60 years, 25% were female, and 44% were white. The median time post-transplant to infection was 5.6 years. Overall, 15% died, 64% required hospital admission, and 7% remained asymptomatic. During the course of illness, only 57% of patients had a fever, and gastrointestinal symptoms were common. Tachypnea, oxygen requirement, elevated creatinine and inflammatory markers were predictive of severe course. Age ≥ 60 was associated with higher risk of death and the use of the combination of calcineurin inhibitor, antimetabolite, and prednisone was associated with more severe disease compared to the combination of calcineurin inhibitor and antimetabolite alone (adjusted OR = 7.3, 95% CI 1.8-36.2). Among hospitalized patients, 30% were treated for secondary infection, acute kidney injury was common and 17% required new renal replacement therapy.
Conclusions: We present the largest study to date of heart transplant patients with COVID-19 showing common atypical presentations and a high case fatality rate of 24% among hospitalized patients and 16% among symptomatic patients.
Keywords: coronavirus disease 2019; epidemiology; heart transplant; hospitalization; mortality; outcomes.
Copyright © 2021 International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Covid-19 in recipients of heart and lung transplantation: Learning from experience.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2021 Sep;40(9):948-950. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2021.05.021. Epub 2021 Jun 9. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34246563 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Levin AT, Hanage WP, Owusu-Boaitey N, Cochran KB, Walsh SP, Meyerowitz-Katz G. Assessing the age specificity of infection fatality rates for COVID-19: systematic review, meta-analysis, and public policy implications. Eur J Epidemiol. 2020;35:1123–1138. doi: 10.1007/s10654-020-00698-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

