Common genetic variation influencing human white matter microstructure
- PMID: 34140357
- PMCID: PMC8370718
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abf3736
Common genetic variation influencing human white matter microstructure
Abstract
Brain regions communicate with each other through tracts of myelinated axons, commonly referred to as white matter. We identified common genetic variants influencing white matter microstructure using diffusion magnetic resonance imaging of 43,802 individuals. Genome-wide association analysis identified 109 associated loci, 30 of which were detected by tract-specific functional principal components analysis. A number of loci colocalized with brain diseases, such as glioma and stroke. Genetic correlations were observed between white matter microstructure and 57 complex traits and diseases. Common variants associated with white matter microstructure altered the function of regulatory elements in glial cells, particularly oligodendrocytes. This large-scale tract-specific study advances the understanding of the genetic architecture of white matter and its genetic links to a wide spectrum of clinical outcomes.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures

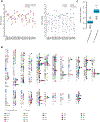

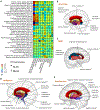
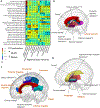

Comment in
-
White matter and human behavior.Science. 2021 Jun 18;372(6548):1265-1266. doi: 10.1126/science.abj1881. Science. 2021. PMID: 34140371 No abstract available.
References
-
- Koziol LF, Budding DE, Chidekel D, Adaptation, expertise, and giftedness: towards an understanding of cortical, subcortical, and cerebellar network contributions. The Cerebellum 9, 499–529 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041093/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103573/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA041123/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH110921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089924/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109677/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041106/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041117/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 MH089983/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA041147/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH116442/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH116527/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041120/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041134/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041022/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH086633/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041156/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041025/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD079124/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MH091657/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041089/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041028/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041048/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG050986/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041148/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA041174/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DA029475/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

