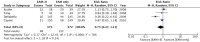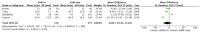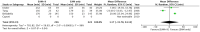Impact of image integration on clinical and procedural outcomes of radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 34141006
- PMCID: PMC8207379
- DOI: 10.1002/joa3.12508
Impact of image integration on clinical and procedural outcomes of radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this meta-analysis was to evaluate the impact of image integration technique on clinical and procedural outcomes in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation with a three-dimensional electroanatomic mapping system.
Methods: Randomized controlled trials were identified through a systematic literature search of PubMed and CENTRAL databases from inception to April 2020. The primary outcome was arrhythmia recurrence during the follow-up period. The secondary outcomes were the difference in total procedural time and fluoroscopy time.
Results: Four studies with a total of 749 patients were included. The pooled result showed no statistically significant difference between the groups with respect to arrhythmia recurrence (RR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.47-1.21), fluoroscopy time (MD, -6 minutes; 95% CI, -23.4 to 11.3), and total procedural time (MD, 1.1 minutes; 95% CI, -31.8 to 34.1).
Conclusion: Image integration to guide radiofrequency catheter ablation for patients with atrial fibrillation does not improve clinical and procedural outcomes.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; catheter ablation; electroanatomic mapping; image integration; pulmonary vein isolation.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Arrhythmia published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of the Japanese Heart Rhythm Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Haïssaguerre M, Jaïs P, Shah DC, et al. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(10):659–66. - PubMed
-
- Calkins H, Kuck KH, Cappato R, et al. 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection. Procedural Techniques, Patient Management and Follow‐up, Definitions, Endpoints, and Research Trial Design EP Eur. 2012;14(4):528–606. - PubMed
-
- Dong J, Calkins H, Solomon SB, et al. Integrated electroanatomic mapping with three‐dimensional computed tomographic images for real‐time guided ablations. Circulation. 2006;113(2):186–94. - PubMed
-
- Kistler PM, Rajappan K, Jahngir M, et al. The impact of CT image integration into an electroanatomic mapping system on clinical outcomes of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006;17(10):1093–101. - PubMed
-
- Kistler PM, Rajappan K, Harris S, et al. The impact of image integration on catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation using electroanatomic mapping: a prospective randomized study. Eur Heart J. 2008;29(24):3029–36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous