The effects of hemsball on the motor proficiency of students with intellectual disabilities
- PMID: 34141372
- PMCID: PMC8132925
- DOI: 10.1080/20473869.2018.1488534
The effects of hemsball on the motor proficiency of students with intellectual disabilities
Abstract
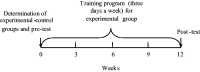
Objective: The effects of hemsball game skills development program on the motor proficiency level of children in the 12-16 age group with mild and moderate intellectual disabilities (ID) have been examined in this study. Method: A total of 50 (25 experimental group +25 control group) students, 23 of which had mild intellectual disabilities (ID) and 27 with moderate ID studying in special education classes in the schools in Afyonkarahisar province in Turkey participated in the study. While no training was given to the control group, the students in the experimental group were subjected to 60 min of applications involving a basic hemsball training program per day for 3 days per week throughout 12 weeks. Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency (BOT-2) sub-tests (balance, bilateral coordination, upper-limb coordination) were applied twice, once before starting the program (pre-test) and once after the program was completed (post-test). The obtained data were tested with paired-samples t-test and independent-samples t-test. Result and Conclusion: As a result of the study, it was noted that the application of the hemsball game skill development program had incurred significant differences between the experimental and control group according to the post-test as well as the pre-test and post-test for the experimental group which were positive. However, it was determined that the application was more effective in students with moderate level ID than students with mild ID.
Keywords: BOT-2; Hemsball; intellectual disabilities (ID); motor proficiency.
© 2018 The British Society of Developmental Disabilities.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Motor proficiency differences among students with intellectual disabilities, autism, and developmental disability.J Exerc Rehabil. 2018 Apr 26;14(2):275-281. doi: 10.12965/jer.1836046.023. eCollection 2018 Apr. J Exerc Rehabil. 2018. PMID: 29740563 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of a motor intervention programme for learners identified with moderate to severe intellectual disabilities.Heliyon. 2022 Oct 20;8(10):e11165. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11165. eCollection 2022 Oct. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36303914 Free PMC article.
-
Motor proficiency of learners with moderate to severe intellectual disabilities.Afr J Disabil. 2024 Feb 21;13:1262. doi: 10.4102/ajod.v13i0.1262. eCollection 2024. Afr J Disabil. 2024. PMID: 38445071 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the fundamental movement skill proficiency of children with intellectual disabilities and typically developing children: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Intellect Disabil Res. 2023 Dec;67(12):1336-1353. doi: 10.1111/jir.13012. Epub 2023 Feb 14. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2023. PMID: 36788023
-
Motor competence assessments for children with intellectual disabilities and/or autism: a systematic review.BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2020 Nov 19;6(1):e000902. doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2020-000902. eCollection 2020. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2020. PMID: 33324486 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Social exercise interventions for children who have complex developmental needs: A systematic review.J Child Health Care. 2025 Mar;29(1):245-287. doi: 10.1177/13674935231190984. Epub 2023 Jul 20. J Child Health Care. 2025. PMID: 37471588 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of training on variability and accuracy of overhand throwing in children with Down syndrome.Int J Dev Disabil. 2019 Jul 26;67(4):237-244. doi: 10.1080/20473869.2019.1574388. eCollection 2021. Int J Dev Disabil. 2019. PMID: 34408858 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits of inclusive sport training on fitness and health of athletes with and without intellectual disability.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 11;14(1):21203. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69334-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39261519 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of adapted physical activity on the motor development of children with mild intellectual disability.Int J Dev Disabil. 2024 Apr 11;71(5):777-787. doi: 10.1080/20473869.2024.2332751. eCollection 2025. Int J Dev Disabil. 2024. PMID: 40687529 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a 12-week structured circuit exercise program on physical fitness levels of children with autism spectrum condition and typically developing children.Int J Dev Disabil. 2020 Sep 17;68(4):500-510. doi: 10.1080/20473869.2020.1819943. eCollection 2022. Int J Dev Disabil. 2020. PMID: 35937176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arslan, E. and Ince, G. 2015. The effects of 12 weeks exercise program on the level of gross motor skill of the children with atypical autism. International Journal of Sports, Exercise and Training Science, 1, 51–62. doi:10.18826/ijsets.66769. - DOI
-
- Bruininks, R. H. and Bruininks, B. 2005. Bruininks-Oseretsky test of motor proficiency (2nd ed.). Minneapolis, MN: NCS Pearson.
-
- Bruininks, R. H. and Chavat, M. 1990. Research on the motor proficiency of persons with mental retardation, psychomotor therapy and adapted physical activity. (Ed: Coppenolle H. V. and Simons J.). In Better Movement Proceeding of the 2 International Symposium, Belgium: 43–69.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials