Giant versus regular parathyroid adenoma: A retrospective comparative study
- PMID: 34141425
- PMCID: PMC8188251
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102454
Giant versus regular parathyroid adenoma: A retrospective comparative study
Abstract
Background: A fraction of Parathyroid Adenoma (PTA) is considered giant if they weigh more than 3.5 g. There is no clear consensus whether this subgroup has a distinct clinical or biochemical presentation that could have implications on PTA localization and management. In this study, we investigate the difference between regular and giant PTA patients regarding their clinical and laboratory findings as well as their postoperative outcomes.
Materials and methods: Clinical and PTA-related data were retrospectively retrieved from all patients undergoing parathyroidectomy from 2010 to 2019 at our hospital.
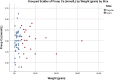
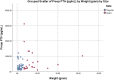
Results: A total number of 84 PTA (Females 76.2%) patients were included, of which 24 (28.6%) qualified as a giant with a mean weight of 7.86 g and the rest were regular adenomas (71.4%) with a mean weight of 1.45 g. Giant adenomas were more likely to present at a younger age compared to regular adenoma patients, (44.4 vs 50.8, P = 0.053, D = 0.470). Preoperative PTH levels were significantly higher in the giant PTA group (650.8 vs 334.2 pg/mL, P = 0.044, r = 0.22). Hospital stay was on average 1.6 days longer in giant PTA patients compared to regular PTA patients.
Conclusion: Giant PTA compromised a significant percentage of all adenomas, which was higher than what is reported in the literature and might reflect a delay in diagnosis and lack of screening tests. Both giant and regular adenomas seem to run a similar clinical course, yet biochemical abnormalities in PTH levels may have a predictive value for adenoma weight.
Keywords: Calcium; PTH; Parathyroid adenoma; Parathyroidectomy; Primary hyperparathyroidism.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Silverberg S.J., Shane E., Jacobs T.P., Siris E., Bilezikian J.P. A 10-year prospective study of primary hyperparathyroidism with or without parathyroid surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999 Oct;341(17):1249–1255. - PubMed
-
- Baloch Z.W., Livolsi V.A. Bilezikian JPBT-TP. Third E. Academic Press; San Diego: 2015. Chapter 1 - parathyroids: morphology and pathology; pp. 23–36.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123971661000011 Available from:
-
- Wolfe S.A., Sharma S. Treasure Island. FL); 2020. Parathyroid adenoma.
-
- Neagoe R.M., Sala D.T., Borda A., Mogoantă C.A., Műhlfay G. Clinicopathologic and therapeutic aspects of giant parathyroid adenomas - three case reports and short review of the literature. Rom J Morphol Embryol = Rev Roum Morphol Embryol. 2014;55(2 Suppl):669–674. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources