The gut microbiome of the Sunda pangolin (Manis javanica) reveals its adaptation to specialized myrmecophagy
- PMID: 34141474
- PMCID: PMC8179220
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.11490
The gut microbiome of the Sunda pangolin (Manis javanica) reveals its adaptation to specialized myrmecophagy
Abstract
Background: The gut microbiomes of mammals are closely related to the diets of their hosts. The Sunda pangolin (Manis javanica) is a specialized myrmecophage, but its gut microbiome has rarely been studied.
Methods: Using high-throughput Illumina barcoded 16S rRNA amplicons of nine fecal samples from nine captive Sunda pangolins, we investigated their gut microbiomes.
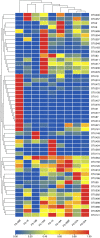
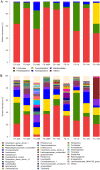
Results: The detected bacteria were classified into 14 phyla, 24 classes, 48 orders, 97 families, and 271 genera. The main bacterial phyla were Firmicutes (73.71%), Proteobacteria (18.42%), Actinobacteria (3.44%), and Bacteroidetes (0.51%). In the PCoA and neighbor-net network (PERMANOVA: pangolins vs. other diets, weighted UniFrac distance p < 0.01, unweighted UniFrac distance p < 0.001), the gut microbiomes of the Sunda pangolins were distinct from those of mammals with different diets, but were much closer to other myrmecophages, and to carnivores, while distant from herbivores. We identified some gut microbiomes related to the digestion of chitin, including Lactococcus, Bacteroides, Bacillus, and Staphylococcus species, which confirms that the gut microbiome of pangolins may help them to digest chitin.
Significance: The results will aid studies of extreme dietary adaption and the mechanisms of diet differentiation in mammals, as well as metagenomic studies, captive breeding, and ex situ conservation of pangolins.
Keywords: 16S rRNA sequencing; Convergence; Gut microbiome; Myrmecophage; Pholidota.
©2021 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Allali I, Arnold JW, Roach J, Cadenas MB, Butz N, Hassan HM, Koci M, Ballou A, Mendoza M, Ali R, Azcarate-Peril MA. A comparison of sequencing platforms and bioinformatics pipelines for compositional analysis of the gut microbiome. BMC Microbiology. 2017;17:194. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-1101-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Almonacid DE, Kraal L, Ossandon FJ, Budovskaya YV, Cardenas JP, Bik EM, Goddard AD, Richman J, Apte ZS. 16S rRNA gene sequencing and healthy reference ranges for 28 clinically relevant microbial taxa from the human gut microbiome. PLOS ONE. 2017;12:e0176555. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176555. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anand AAP, Vennison SJ, Sankar SG, Prabhu DIG, Vasan PT, Raghuraman T, Geoffrey CJ, Vendan SE. Isolation and characterization of bacteria from the gut of Bombyx mori that degrade cellulose, xylan, pectin and starch and their impact on digestion. Journal of Insect Science. 2010;10:107. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

