Mistranslation Drives Alterations in Protein Levels and the Effects of a Synonymous Variant at the Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Locus
- PMID: 34141520
- PMCID: PMC8188187
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202004168
Mistranslation Drives Alterations in Protein Levels and the Effects of a Synonymous Variant at the Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Locus
Abstract
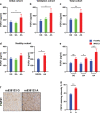
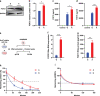
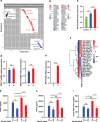
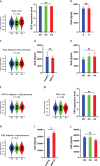
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a liver-derived hormone with pleiotropic beneficial effects on metabolism. Paradoxically, FGF21 levels are elevated in metabolic diseases. Interventions that restore metabolic homeostasis reduce FGF21. Whether abnormalities in FGF21 secretion or resistance in peripheral tissues is the initiating factor in altering FGF21 levels and function in humans is unknown. A genetic approach is used to help resolve this paradox. The authors demonstrate that the primary event in dysmetabolic phenotypes is the elevation of FGF21 secretion. The latter is regulated by translational reprogramming in a genotype- and context-dependent manner. To relate the findings to tissues outcomes, the minor (A) allele of rs838133 is shown to be associated with increased hepatic inflammation in patients with metabolic associated fatty liver disease. The results here highlight a dominant role for translation of the FGF21 protein to explain variations in blood levels that is at least partially inherited. These results provide a framework for translational reprogramming of FGF21 to treat metabolic diseases.
Keywords: fibroblast growth factor 21; genetics; metabolic; metabolic associated fatty liver disease.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21: update on genetics and molecular biology.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2025 Apr 1;36(2):88-95. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000960. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2025. PMID: 39450972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 levels are increased in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients and are correlated with hepatic triglyceride.J Hepatol. 2010 Nov;53(5):934-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.05.018. Epub 2010 Jul 17. J Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20675007
-
The FGF21 response to fructose predicts metabolic health and persists after bariatric surgery in obese humans.Mol Metab. 2017 Nov;6(11):1493-1502. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 29107295 Free PMC article.
-
Increased fibroblast growth factor 21 in obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Gastroenterology. 2010 Aug;139(2):456-63. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.04.054. Epub 2010 May 5. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20451522 Free PMC article.
-
Potential roles of fibroblast growth factor 21 in the brain.Metab Brain Dis. 2016 Apr;31(2):239-48. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9789-3. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Metab Brain Dis. 2016. PMID: 26738728 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteome profiling to advance management of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024 Feb 1;13(1):147-149. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-596. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38322223 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21: update on genetics and molecular biology.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2025 Apr 1;36(2):88-95. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000960. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2025. PMID: 39450972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A literature review of genetics and epigenetics of HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma: translational impact.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024 Aug 1;13(4):650-661. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-562. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39175720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards precision medicine in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2023 Oct;24(5):885-899. doi: 10.1007/s11154-023-09820-6. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 37477772 Review.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 is a hepatokine involved in MASLD progression.United European Gastroenterol J. 2024 Oct;12(8):1056-1068. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12534. Epub 2024 Jun 18. United European Gastroenterol J. 2024. PMID: 38894596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang X., Yeung D. C., Karpisek M., Stejskal D., Zhou Z.‐G., Liu F., Wong R. L., Chow W.‐S., Tso A. W., Lam K. S., Diabetes 2008, 57, 1246. - PubMed
