A Dynamic Aspartate-to-Alanine Aminotransferase Ratio Provides Valid Predictions of Incident Severe Liver Disease
- PMID: 34141987
- PMCID: PMC8183175
- DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1700
A Dynamic Aspartate-to-Alanine Aminotransferase Ratio Provides Valid Predictions of Incident Severe Liver Disease
Abstract
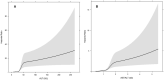
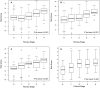
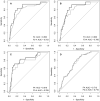
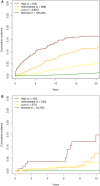
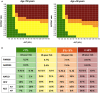
The aspartate-to-alanine aminotransferase ratio (AAR) is associated with liver fibrosis, but its predictive performance is suboptimal. We hypothesized that the association between AAR and liver disease depends on absolute transaminase levels and developed and validated a model to predict liver-related outcomes in the general population. A Cox regression model based on age, AAR, and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level (dynamic AAR [dAAR]) using restricted cubic splines was developed in Finnish population-based health-examination surveys (FINRISK, 2002-2012; n = 18,067) with linked registry data for incident liver-related hospitalizations, hepatocellular carcinoma, or liver death. The model was externally validated for liver-related outcomes in a Swedish population cohort (Swedish Apolipoprotein Mortality Risk [AMORIS] subcohort; n = 126,941) and for predicting outcomes and/or prevalent fibrosis/cirrhosis in biopsied patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), chronic hepatitis C, or alcohol-related liver disease (ALD). The dynamic AAR model predicted liver-related outcomes both overall (optimism-corrected C-statistic, 0.81) and in subgroup analyses of the FINRISK cohort and identified persons with >10% risk for liver-related outcomes within 10 years. In independent cohorts, the C-statistic for predicting liver-related outcomes up to a 10-year follow-up was 0.72 in the AMORIS cohort, 0.81 in NAFLD, and 0.75 in ALD. Area-under-the-curve (AUC) for detecting prevalent cirrhosis was 0.80-0.83 in NAFLD, 0.80 in hepatitis C, but only 0.71 in ALD. In ALD, model performance improved when using aspartate aminotransferase instead of ALT in the model (C-statistic, 0.84 for outcome; AUC, 0.82 for prevalent cirrhosis). Conclusion: A dAAR score provides prospective predictions for the risk of incident severe liver outcomes in the general population and helps detect advanced liver fibrosis/cirrhosis. The dAAR score could potentially be used for screening the unselected general population and as a trigger for further liver evaluations.
© 2021 The Authors. Hepatology Communications published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Ioannou GN, Boyko EJ, Lee SP. The prevalence and predictors of elevated serum aminotransferase activity in the United States in 1999‐2002. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101:76‐82. - PubMed
-
- Caballeria L, Pera G, Arteaga I, Rodriguez L, Aluma A, Morillas RM, et al. High prevalence of liver fibrosis among European adults with unknown liver disease: a population‐based study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;16:1138‐1145.e5. - PubMed
-
- Donnan PT, McLernon D, Dillon JF, Ryder S, Roderick P, Sullivan F, et al. Development of a decision support tool for primary care management of patients with abnormal liver function tests without clinically apparent liver disease: a record‐linkage population cohort study and decision analysis (ALFIE). Health Technol Assess 2009;13:iii‐iv, ix‐xi, 1‐134. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

