Efficacy and safety of switching from reference adalimumab to CT-P17 (100 mg/ml): 52-week randomized, double-blind study in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 34142111
- PMCID: PMC8996790
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab460
Efficacy and safety of switching from reference adalimumab to CT-P17 (100 mg/ml): 52-week randomized, double-blind study in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To compare the safety and efficacy of switching from reference adalimumab to adalimumab biosimilar CT-P17 with continuing reference adalimumab/CT-P17 in active RA.
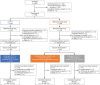
Methods: This double-blind, phase III study randomized (1:1) subjects with active RA to receive 40 mg (100 mg/ml) CT-P17 or European Union-sourced reference adalimumab subcutaneously every 2 weeks (Q2W) until week (W) 24 [treatment period (TP) 1]. Thereafter, subjects receiving reference adalimumab were randomized (1:1) to continue reference adalimumab or switch to CT-P17 from W26 (both Q2W until W48; TP2). Subjects receiving CT-P17 in TP1 continued CT-P17. W0-W24 results were previously reported; we present W26-W52 findings. End points were efficacy (including joint damage progression), pharmacokinetics, safety and immunogenicity.
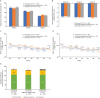
Results: Of 607 subjects who initiated TP2 treatment, 303 continued CT-P17, 153 continued reference adalimumab and 151 switched to CT-P17. Efficacy improvements up to W24 were maintained during TP2; efficacy was comparable among groups. At W52, 20% improvement in ACR response rates were 80.5% (continued CT-P17), 77.8% (continued reference adalimumab) and 82.2% (switched to CT-P17). Joint damage progression was minimal. Mean trough serum adalimumab concentrations were similar among groups. CT-P17 and reference adalimumab safety profiles were numerically similar and switching did not affect immunogenicity. At W52, 28.4% (continued CT-P17), 27.0% (continued reference adalimumab) and 28.3% (switched to CT-P17) of subjects were anti-drug antibody-positive.
Conclusion: Efficacy, pharmacokinetics, safety and immunogenicity of CT-P17 and reference adalimumab were comparable after 1 year of treatment, including after switching from reference adalimumab to CT-P17.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, http://clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03789292.
Keywords: CT-P17; adalimumab; biosimilar; efficacy; immunogenicity; rheumatoid arthritis; safety; switching; tumour necrosis factor inhibitors.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Rheumatology: biosimilars are here to stay.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022 Apr 11;61(4):1312-1313. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab663. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022. PMID: 34559204 No abstract available.
References
-
- European Medicines Agency. Yuflyma summary of product characteristics. 2021. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/yuflyma-epar-....
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. Conduct of clinical trials of medical products during COVID-19 public health emergency: Guidance for industry, investigators, and institutional review boards. 2020. https://www.fda.gov/media/136238/download (15 April 2021, date last acce....

