Increased transmissibility and global spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern as at June 2021
- PMID: 34142653
- PMCID: PMC8212592
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.24.2100509
Increased transmissibility and global spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern as at June 2021
Abstract
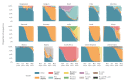
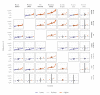
We present a global analysis of the spread of recently emerged SARS-CoV-2 variants and estimate changes in effective reproduction numbers at country-specific level using sequence data from GISAID. Nearly all investigated countries demonstrated rapid replacement of previously circulating lineages by the World Health Organization-designated variants of concern, with estimated transmissibility increases of 29% (95% CI: 24-33), 25% (95% CI: 20-30), 38% (95% CI: 29-48) and 97% (95% CI: 76-117), respectively, for B.1.1.7, B.1.351, P.1 and B.1.617.2.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Variants of concern; Variants of interest.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update, 1 June 2021. Geneva: WHO; 2021. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/341622
-
- Department of Health and Social Care. New measures to boost response to the B1.617.2 variant. Press release. London: GOV.UK; 13 May 2021. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/new-measures-to-boost-response-to-the...
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). COVID data tracker. Atlanta: CDC. [Accessed: 13 Apr 2021]. Available from: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker
-
- Public Health England (PHE). Investigation of novel SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: technical briefings. London: PHE; 2021. [Accessed: 13 Apr 2021]. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/investigation-of-novel-sars-c...
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
