Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with either treatment-naive or previously treated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (Study 111/KEYNOTE-146): a phase 1b/2 study
- PMID: 34143969
- PMCID: PMC8316679
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00241-2
Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with either treatment-naive or previously treated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (Study 111/KEYNOTE-146): a phase 1b/2 study
Abstract
Background: Despite advances in the first-line treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC), there is an unmet need for options to address disease progression during or after treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Pembrolizumab and lenvatinib are active as monotherapies in RCC; thus, we aimed to evaluate the combination of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in these patients.
Methods: We report results of the metastatic RCC cohort from an open-label phase 1b/2 study of lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab in patients aged at least 18 years with selected solid tumours and an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0-1. Oral lenvatinib at 20 mg was given once daily along with intravenous pembrolizumab at 200 mg once every 3 weeks. Patients remained on study drug treatment until disease progression, development of unacceptable toxicity, or withdrawal of consent. Efficacy was analysed in patients with clear cell metastatic RCC receiving study drug by previous therapy grouping: treatment naive, previously treated ICI naive (previously treated with at least one line of therapy but not with an anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 ICI), and ICI pretreated (ie, anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1) patients. Safety was analysed in all enrolled and treated patients. The primary endpoint was the objective response rate at week 24 per immune-related Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (irRECIST) by investigator assessment. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02501096) and with the EU Clinical Trials Register (EudraCT2017-000300-26), and is closed to new participants.
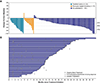
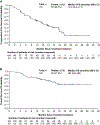
Findings: Between July 21, 2015, and Oct 16, 2019, 145 patients were enrolled in the study. Two patients had non-clear cell RCC and were excluded from the efficacy analysis (one in the treatment-naive group and one in the ICI-pretreated group); thus, the population evaluated for efficacy comprised 143 patients (n=22 in the treatment-naive group, n=17 in the previously treated ICI-naive group, and n=104 in the ICI-pretreated group). All 145 enrolled patients were included in the safety analysis. The median follow-up was 19·8 months (IQR 14·3-28·4). The number of patients with an objective response at week 24 by irRECIST was 16 (72·7%, 95% CI 49·8-89·3) of 22 treatment-naive patients, seven (41·2%, 18·4-67·1) of 17 previously treated ICI-naive patients, and 58 (55·8%, 45·7-65·5) of 104 ICI-pretreated patients. Of 145 patients, 82 (57%) had grade 3 treatment-related adverse events and ten (7%) had grade 4 treatment-related adverse events. The most common grade 3 treatment-related adverse event was hypertension (30 [21%] of 145 patients). Treatment-related serious adverse events occurred in 36 (25%) patients, and there were three treatment-related deaths (upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage, sudden death, and pneumonia).
Interpretation: Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab showed encouraging antitumour activity and a manageable safety profile and might be an option for post-ICI treatment of metastatic RCC.
Funding: Eisai and Merck Sharp & Dohme.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C-HL received support for this Article from Eisai and Merck; grants or contracts to their institution from Eisai and Merck; consulting fees from Eisai and Merck; for attending meetings and travel from Eisai; and fees for participation in a scientific advisory committee for Merck; consulting fees from Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Pfizer, and EMD Serono; honoraria from AiCME, Intellisphere, and Research to Practice; research funds to the institute from Bristol Myers Squibb, Calithera, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Exelixis, Merck, and Pfizer. AYS participated on an advisory board for Eisai, Exelixis, Pfizer, and Roche; and received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, and EMD Serono. DR received support for this Article from Eisai. AR received grants or contracts to their institution from Eisai and Merck; consulting fees to their institution from Eli Lilly; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers' bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from Bayer, Cardinal Health, Eli Lilly, and Sanofi; and research funding to their institution from Clovis Oncology, Eli Lilly, Pfizer/Astellas, and Seattle Genetics/Astellas. MHT received clinical research funding for the present work to their institution from Eisai; and honoraria for participation in advisory boards and speakers' bureaus from Eisai. JJH received grants or contracts from Merck; consulting fees from BostonGene and Eisai; support for attending meetings or travel, or both from Elsevier; and stock or stock options from BostonGene. AP received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers' bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from Bristol Myers Squibb, Ipsen, and Pfizer; and support for attending meetings or travel, or both, from Bristol Myers Squibb and Pfizer. RGS received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers' bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, and Roche; support for attending meetings or travel, or both, from MSD-Merck and Pfizer; and participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board from Bristol Myers Squibb. ALC received consulting fees from Amgen; and payment for expert testimony from the Department of Justice. NJV received support for this Article, including provision of study patients, payments to institution, medical writing, and manuscript writing charges from Eisai and Merck; consulting fees from Eisai and Merck; and payment for legal testimony from Merck. MAB received grants or contracts to their institution from Advanced Accelerator Applications, a Novartis Company, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech/Roche, Genome & Company, Incyte, Nektar, Peloton Therapeutics, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Tricon Pharmaceuticals, and Xencor; honoraria for participation in a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calithera Biosciences, Eisai, Exelixis, Genomic Health, Janssen, Nektar, Pfizer, and Sanofi. ØKT received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers' bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Astellas and Bristol Myers Squibb; and fees for participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for Bayer. RFS received grants or contracts to their institution from AbbVie, Aduro, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, CytomX, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Genentech/Roche, Immunocore, Merck, Mirati, Moderna, Novartis, and QED therapeutics; consulting fees from Aduro, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, EMD Serono, Exelixis, Janssen, Mirati, Pfizer, Puma, and Seattle Genetics; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Exelixis, Pfizer, and Seattle Genetics; support for attending meetings or travel, or both, from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eisai, Exelixis, Mirati; and patents pending, PCT/US2020/031357 on neoantigens in cancer. DH received support for this Article to their institution from Eisai; consulting fees from Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Eisai, Ipsen, Janssen-Cilag, and Roche; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Advanced Accelerator Applications, a Novartis Company, Astellas, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Ipsen, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Sanofi; and participation on an advisory board for Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Eisai, Ipsen, Janssen-Cilag, and Roche; SJ has stock or stock options in Merck. EVS and RFP are employed by, and have stock or stock options in, Merck. JW and PK are employed by Eisai. CEO and ADS are employed by Eisai Europe. RJM received support for the present Article from Eisai and Merck; grants or contracts from Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Aveo Pharmaceuticals, EMD Serono, Exelixis, Genentech, Incyte, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; and support for attending meetings or travel, or both, from Bristol Myers Squibb. CDS, DRS, SGR, MG, DR, and JC declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ. Systemic therapy for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2017; 376: 354–66. - PubMed
-
- European Association of Urology. Renal Cell Carcinoma Guidelines 2020. Summary of Changes. https://uroweb.org/guideline/renal-cell-carcinoma/?type=summary-of-changes (accessed 3 Mar 2021).
-
- Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V, et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2019; 380: 1116–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

