Ultrasound evaluation of the hands and wrists in patients with systemic sclerosis: Osteophytosis is a major contributor to tender joints
- PMID: 34144383
- PMCID: PMC8384688
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.04.020
Ultrasound evaluation of the hands and wrists in patients with systemic sclerosis: Osteophytosis is a major contributor to tender joints
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the prevalence and clinical associations of ultrasound (US) findings of inflammatory arthritis and joint and soft tissue pathology in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc).
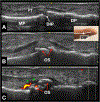
Methods: The hands and wrists of 43 SSc patients and 35 age-balanced controls were evaluated by clinical exam and musculoskeletal US. Synovial and tenosynovial pathology were assessed using semi-quantitative Gray Scale (GS) and Power Doppler (PD) scoring. US evaluation for osteophytes, erosions, ulnar artery occlusion, and median nerve cross-sectional areas was performed. Tender joints (TJ), swollen joints (SJ), modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS), digital ulcers, contractures, and calcinosis were evaluated. Concordance between US and physical exam findings at each joint region were assessed, and associations between their severity were analyzed.
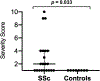
Results: TJs and SJs were present in 44.2% and 62.8% of SSc patients, respectively. Inflammatory arthritis, defined as having both GS>0 and PD>0, was observed in 18.6% of SSc patients and no controls. There was a high concordance by joint region between GS synovial hypertrophy and osteophytes (κ=0.88) as well as TJs (κ=0.72). SSc patients had more osteophytes compared to controls (48.8% vs 22.9%, p = 0.018) as well as higher osteophyte severity (p = 0.033).
Conclusions: Despite a high percentage of tender and swollen joints, less than 20% of SSc patients met criteria for inflammatory arthritis on US. The high concordance of osteophytes with GS synovial hypertrophy and tender joints suggest that osteophytosis may be a significant contributor to joint pain in SSc patients.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures

Comment in
-
Response letter to the editor.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022 Feb;52:151890. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.07.019. Epub 2021 Aug 1. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022. PMID: 34404512 No abstract available.
-
Synovitis and tenosynovitis of the hands and wrists in patients with SSc: The need for a consensus definition of sclerosing tenosynovitis.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022 Feb;52:151901. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.08.009. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022. PMID: 34493395 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cuomo G, Zappia M, Abignano G, Iudici M, Rotondo A, Valentini G. Ultrasonographic features of the hand and wrist in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48(11):1414–1417. - PubMed
-
- Chitale S, Ciapetti A, Hodgson R, et al.Magnetic resonance imaging and musculoskeletal ultrasonography detect and characterize covert inflammatory arthropathy in systemic sclerosis patients with arthralgia. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010;49(12):2357–2361. - PubMed
-
- Avouac J, Walker U, Tyndall A, et al.Characteristics of joint involvement and relationships with systemic inflammation in systemic sclerosis: results from the EULAR Scleroderma Trial and Research Group (EUSTAR) database. J Rheumatol. 2010;37(7):1488–1501. - PubMed
-
- Misra R, Darton K, Jewkes RF, Black CM, Maini RN. Arthritis in scleroderma. Br J Rheumatol. 1995;34(9):831–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

