Genome sequencing of 320 Chinese children with epilepsy: a clinical and molecular study
- PMID: 34145886
- PMCID: PMC8719847
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awab233
Genome sequencing of 320 Chinese children with epilepsy: a clinical and molecular study
Abstract
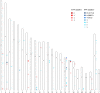
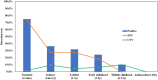
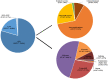
The aim of this study is to evaluate the diagnostic value of genome sequencing in children with epilepsy, and to provide genome sequencing-based insights into the molecular genetic mechanisms of epilepsy to help establish accurate diagnoses, design appropriate treatments and assist in genetic counselling. We performed genome sequencing on 320 Chinese children with epilepsy, and interpreted single-nucleotide variants and copy number variants of all samples. The complete pedigree and clinical data of the probands were established and followed up. The clinical phenotypes, treatments, prognoses and genotypes of the patients were analysed. Age at seizure onset ranged from 1 day to 17 years, with a median of 4.3 years. Pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants were found in 117 of the 320 children (36.6%), of whom 93 (29.1%) had single-nucleotide variants, 22 (6.9%) had copy number variants and two had both single-nucleotide variants and copy number variants. Single-nucleotide variants were most frequently found in SCN1A (10/95, 10.5%), which is associated with Dravet syndrome, followed by PRRT2 (8/95, 8.4%), which is associated with benign familial infantile epilepsy, and TSC2 (7/95, 7.4%), which is associated with tuberous sclerosis. Among the copy number variants, there were three with a length <25 kilobases. The most common recurrent copy number variants were 17p13.3 deletions (5/24, 20.8%), 16p11.2 deletions (4/24, 16.7%), and 7q11.23 duplications (2/24, 8.3%), which are associated with epilepsy, developmental retardation and congenital abnormalities. Four particular 16p11.2 deletions and two 15q11.2 deletions were considered to be susceptibility factors contributing to neurodevelopmental disorders associated with epilepsy. The diagnostic yield was 75.0% in patients with seizure onset during the first postnatal month, and gradually decreased in patients with seizure onset at a later age. Forty-two patients (13.1%) were found to be specifically treatable for the underlying genetic cause identified by genome sequencing. Three of them received corresponding targeted therapies and demonstrated favourable prognoses. Genome sequencing provides complete genetic diagnosis, thus enabling individualized treatment and genetic counselling for the parents of the patients. Genome sequencing is expected to become the first choice of methods for genetic testing of patients with epilepsy.
Keywords: copy number variants; epilepsy; genome sequencing; seizure; single-nucleotide variants.
© The Author(s) (2021). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Figures
Comment in
-
Clinical and genetic spectrum of 355 Chinese children with epilepsy: a trio-sequencing-based study.Brain. 2022 Jun 3;145(5):e43-e46. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac053. Brain. 2022. PMID: 35231114 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Neligan A, Hauser WA, Sander JW. The epidemiology of the epilepsies. Handb Clin Neurol. 2012;107:113–133. - PubMed
-
- Weber YG, Biskup S, Helbig KL, Von Spiczak S, Lerche H. The role of genetic testing in epilepsy diagnosis and management. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2017;17(8):739–750. - PubMed
-
- Steinlein OK, Mulley JC, Propping P, et al. A missense mutation in the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha 4 subunit is associated with autosomal dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy. Nat Genet. 1995;11(2):201–203. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Lin ZJ, Liu L, et al. Epilepsy-associated genes. Seizure. 2017;44:11–20. - PubMed

