Association between PNPLA3 rs738409 polymorphism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34147109
- PMCID: PMC8214766
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-021-00789-4
Association between PNPLA3 rs738409 polymorphism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a common disorder that is known to be the leading cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. This study aims to systematically review and meta-analyze the association between PNPLA3 rs738409 polymorphism and non-alcoholic fatty liver.
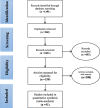
Methods: Following a systematic review and meta-analysis method, articles without any time limitation, were extracted from SID, MagIran, IranDoc, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science (WoS), PubMed and ScienceDirect international databases. Random effects model was used for analysis, and heterogeneity of studies was investigated considering the I2 index and using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software.
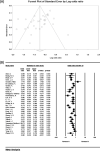
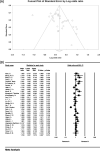
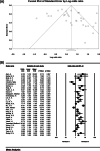
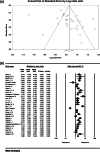
Results: The odds ratio of CC genotype in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver demonstrates the protective effect of CC genotype with the ratio of 0.52, whereas CG genotype presents an increasing effect of CG genotype with the ratio of 0.19, and GG genotype also showed an increasing effect of GG genotype with the ratio of 1.05. Moreover, CG + GG genotypes as a single group demostrated an odds rartio of 0.88.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis highlights that people with CC genotype has 52% lower chance of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and those with CG genotype had 19% higher risk of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver. Those with GG genotype were 105% more likely to develop non-alcoholic fatty liver than others. Moreover, those present in a population with CG + GG genotypes were 88% more likely to have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Keywords: Gene; NAFLD; Non-alcoholic fatty liver; PNPLA3; Polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of PNPLA3 rs738409 G/C gene polymorphism with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: a meta-analysis.BMC Med Genet. 2020 Aug 18;21(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12881-020-01098-8. BMC Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 32811452 Free PMC article.
-
Association between PNPLA3 rs738409 polymorphism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) susceptibility and severity: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Feb;98(7):e14324. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014324. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30762732 Free PMC article.
-
Carriage of the PNPLA3 rs738409 C >G polymorphism confers an increased risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease associated hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2014 Jul;61(1):75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.02.030. Epub 2014 Mar 6. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24607626
-
Association between rs738409 polymorphism in patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (PNPLA3) gene and hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility: Evidence from case-control studies.Gene. 2019 Feb 15;685:143-148. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.11.012. Epub 2018 Nov 4. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30403964 Review.
-
PNPLA3 rs738409 Polymorphism Associated with Hepatic Steatosis and Advanced Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus: A Meta-Analysis.Gut Liver. 2016 May 23;10(3):456-63. doi: 10.5009/gnl15261. Gut Liver. 2016. PMID: 26419236 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in genetic variation in metabolism-related fatty liver disease.Front Genet. 2023 Sep 11;14:1213916. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1213916. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37753315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Race and Ethnicity in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 28;14(21):4556. doi: 10.3390/nu14214556. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36364818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Polymorphisms and Diversity in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A Mini Review.Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 30;11(1):106. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11010106. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36672614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The fatty liver disease-causing protein PNPLA3-I148M alters lipid droplet-Golgi dynamics.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 14:2023.10.13.562302. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.13.562302. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Apr 30;121(18):e2318619121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2318619121. PMID: 37873239 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Alleviation of Hepatic Steatosis by Alpha-Defensin Is Associated with Enhanced Lipolysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 May 19;59(5):983. doi: 10.3390/medicina59050983. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37241215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seko Y, Yamaguchi K, Mizuno N, Okuda K, Takemura M, Taketani H, Hara T, Umemura A, Nishikawa T, Moriguchi M, Yasui K, Kamaguchi M, Nishioji K, Mochizuki N, Kobayashi M, Mori K, Tanaka S, Matsuura K, Tanaka Y, Itoh Y. Combination of PNPLA3 and TLL1 polymorphism can predict advanced fibrosis in Japanese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol. 2018;53(3):438–448. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1372-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tan HL, Zain SM, Mohamed R, Rampal S, Chin KF, Basu RC, Cheah PL, Mahadeva S, Mohamed Z. Association of glucokinase regulatory gene polymorphisms with risk and severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an interaction study with adiponutrin gene. J Gastroenterol. 2014;49(6):1056–1064. doi: 10.1007/s00535-013-0850-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xia MF, Lin HD, Chen LY, Wu L, Ma H, Li Q, Aleteng Q, Hu Y, He WY, Gao J, Bian H, Li XY, Gao X. The PNPLA3 rs738409 C>G variant interacts with changes in body weight over time to aggravate liver steatosis, but reduces the risk of incident type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2019;62(4):644–654. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4805-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

