Using adalimumab serum concentration to choose a subsequent biological DMARD in rheumatoid arthritis patients failing adalimumab treatment (ADDORA-switch): study protocol for a fully blinded randomised superiority test-treatment trial
- PMID: 34147123
- PMCID: PMC8214249
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-021-05358-7
Using adalimumab serum concentration to choose a subsequent biological DMARD in rheumatoid arthritis patients failing adalimumab treatment (ADDORA-switch): study protocol for a fully blinded randomised superiority test-treatment trial
Abstract
Background: A substantial proportion of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients discontinues treatment with tumour necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) due to inefficacy or intolerance. After the failure of treatment with a TNFi, treatment can be switched to another TNFi or a bDMARD with a different mode of action (non-TNFi). Measurement of serum drug concentrations and/or anti-drug antibodies (therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM)) may help to inform the choice for the next step. However, the clinical utility of TDM to guide switching has not been investigated in a randomised test-treatment study.
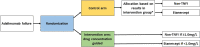
Methods: ADDORA-switch is a 24-week, multi-centre, triple-blinded, superiority test-treatment randomised controlled trial. A total of 84 RA patients failing adalimumab treatment (treatment failure defined as DAS28-CRP > 2.9) will be randomised in a 1:1 ratio to a switching strategy to either TNFi or non-TNFi based on adalimumab serum trough level (intervention group) or random allocation (control group). The primary outcome is the between-group difference in mean time-weighted DAS28 over 24 weeks.
Discussion: The trial design differs in many aspects from previously published and ongoing TDM studies and is considered the first blinded test-treatment trial using TDM in RA. Several choices in the design of this trial are described, and overarching principles regarding test-treatment trials and clinical utility of TDM are discussed in further detail.
Trial registration: Dutch Trial Register NL8210 . Registered on 3 December 2019 (CMO NL69841.091.19).
Keywords: Adalimumab; Anti-TNF; Design; Drug concentration; Rheumatoid arthritis; Switching; Test-treatment trial; Therapeutic drug monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
Michael T. Nurmohamed: consulting fees from AbbVie, Celgene, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Janssen and Sanofi; speaker’s fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Roche and Sanofi; and research funding from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, MSD, Mundipharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and Sanofi. Ronald F van Vollenhoven: research support (institutional grants)—BMS, GSK, Lilly and UCB; support for educational programmes (institutional grants)—Pfizer and Roche; consultancy, for which institutional and/or personal honoraria were received—AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Biotest, Celgene, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Pfizer, Servier and UCB; speaker, for which institutional and/or personal honoraria were received—AbbVie, Galapagos, Janssen, Pfizer and UCB. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adalimumab serum concentration to choose a subsequent biological DMARD in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (ADDORA-switch): results of a blinded randomised test-treatment trial.Ann Rheum Dis. 2025 Aug;84(8):1293-1300. doi: 10.1016/j.ard.2025.03.015. Epub 2025 May 3. Ann Rheum Dis. 2025. PMID: 40318979 Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic drug monitoring of adalimumab in RA: no predictive value of adalimumab serum levels and anti-adalimumab antibodies for prediction of response to the next bDMARD.Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Jul;79(7):867-873. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-216996. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32317314
-
Switching from an anti-TNF monoclonal antibody to soluble TNF-receptor yields better results than vice versa: An observational retrospective study of 72 rheumatoid arthritis switchers.Joint Bone Spine. 2015 Oct;82(5):330-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2015.01.021. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Joint Bone Spine. 2015. PMID: 25864942
-
Optimizing biological treatment in rheumatoid arthritis with the aid of therapeutic drug monitoring.Dan Med J. 2016 Nov;63(11):B5311. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27808043 Review.
-
Sarilumab for Previously-Treated Moderate or Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Evidence Review Group Perspective of a NICE Single Technology Appraisal.Pharmacoeconomics. 2018 Dec;36(12):1427-1437. doi: 10.1007/s40273-018-0677-7. Pharmacoeconomics. 2018. PMID: 29882210 Review.
Cited by
-
Patterns and determinants of response to novel therapies in juvenile and adult-onset polyarthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 Mar 1;63(3):594-607. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead490. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 37725352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartelds GM, Wijbrandts CA, Nurmohamed MT, Stapel S, Lems WF, Aarden L, Dijkmans BAC, Tak PP, Wolbink GJ. Clinical response to adalimumab: relationship to anti-adalimumab antibodies and serum adalimumab concentrations in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(7):921–926. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.065615. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, Nam J, Ramiro S, Voshaar M, van Vollenhoven R, Aletaha D, Aringer M, Boers M, Buckley CD, Buttgereit F, Bykerk V, Cardiel M, Combe B, Cutolo M, van Eijk-Hustings Y, Emery P, Finckh A, Gabay C, Gomez-Reino J, Gossec L, Gottenberg JE, Hazes JMW, Huizinga T, Jani M, Karateev D, Kouloumas M, Kvien T, Li Z, Mariette X, McInnes I, Mysler E, Nash P, Pavelka K, Poór G, Richez C, van Riel P, Rubbert-Roth A, Saag K, da Silva J, Stamm T, Takeuchi T, Westhovens R, de Wit M, van der Heijde D. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(6):960–977. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210715. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schoels M, Aletaha D, Smolen JS, Wong JB. Comparative effectiveness and safety of biological treatment options after tumour necrosis factor α inhibitor failure in rheumatoid arthritis: systematic review and indirect pairwise meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(8):1303–1308. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200490. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Manders SH, Kievit W, Adang E, Brus HL, Moens HJ, Hartkamp A, et al. Cost-effectiveness of abatacept, rituximab, and TNFi treatment after previous failure with TNFi treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: a pragmatic multi-centre randomised trial. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0630-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Torrente-Segarra V, Acosta Pereira A, Morla R, Ruiz JM, Clavaguera T, Figuls R, Corominas H, Geli C, Roselló R, de Agustín JJ, Alegre C, Pérez C, García A, Rodríguez de la Serna A. VARIAR study: assessment of short-term efficacy and safety of rituximab compared to an tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists as second-line drug therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to a first tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonist. Reumatol Clin. 2016;12(6):319–322. doi: 10.1016/j.reuma.2015.11.019. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

