Identification of novel bat coronaviruses sheds light on the evolutionary origins of SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses
- PMID: 34147139
- PMCID: PMC8188299
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.008
Identification of novel bat coronaviruses sheds light on the evolutionary origins of SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses
Abstract
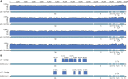
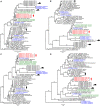
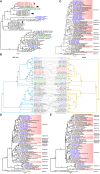
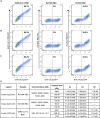
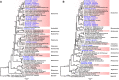
Despite the discovery of animal coronaviruses related to SARS-CoV-2, the evolutionary origins of this virus are elusive. We describe a meta-transcriptomic study of 411 bat samples collected from a small geographical region in Yunnan province, China, between May 2019 and November 2020. We identified 24 full-length coronavirus genomes, including four novel SARS-CoV-2-related and three SARS-CoV-related viruses. Rhinolophus pusillus virus RpYN06 was the closest relative of SARS-CoV-2 in most of the genome, although it possessed a more divergent spike gene. The other three SARS-CoV-2-related coronaviruses carried a genetically distinct spike gene that could weakly bind to the hACE2 receptor in vitro. Ecological modeling predicted the co-existence of up to 23 Rhinolophus bat species, with the largest contiguous hotspots extending from South Laos and Vietnam to southern China. Our study highlights the remarkable diversity of bat coronaviruses at the local scale, including close relatives of both SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; bats; coronavirus; evolution; phylogeny; porcine epidemic diarrhea virus; spike protein; swine acute diarrhea syndrome.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Comment in
-
Searching for relatives of SARS-CoV-2 in bats.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021 Aug;19(8):482. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00595-8. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34145421 Free PMC article.
-
Virus hunters: Discovering the evolutionary origins of SARS-CoV-2.Cell Host Microbe. 2021 Jul 14;29(7):1031-1033. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.06.012. Cell Host Microbe. 2021. PMID: 34265239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Charleston M.A. 2011. TreeMap 3b.http://sites.google.com/ site/cophylogeny accessed 14 Jul 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

