Interferon-Gamma-Producing CD8+ Tissue Resident Memory T Cells Are a Targetable Hallmark of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Colitis
- PMID: 34147519
- PMCID: PMC8527886
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.06.025
Interferon-Gamma-Producing CD8+ Tissue Resident Memory T Cells Are a Targetable Hallmark of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Colitis
Abstract
Background & aims: The pathogenesis of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-colitis remains incompletely understood. We sought to identify key cellular drivers of ICI-colitis and their similarities to idiopathic ulcerative colitis, and to determine potential novel therapeutic targets.
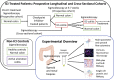
Methods: We used a cross-sectional approach to study patients with ICI-colitis, those receiving ICI without the development of colitis, idiopathic ulcerative colitis, and healthy controls. A subset of patients with ICI-colitis were studied longitudinally. We applied a range of methods, including multiparameter and spectral flow cytometry, spectral immunofluorescence microscopy, targeted gene panels, and bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing.
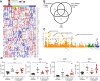
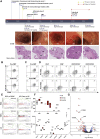
Results: We demonstrate CD8+ tissue resident memory T (TRM) cells are the dominant activated T cell subset in ICI-colitis. The pattern of gastrointestinal immunopathology is distinct from ulcerative colitis at both the immune and epithelial-signaling levels. CD8+ TRM cell activation correlates with clinical and endoscopic ICI-colitis severity. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis confirms activated CD8+ TRM cells express high levels of transcripts for checkpoint inhibitors and interferon-gamma in ICI-colitis. We demonstrate similar findings in both anti-CTLA-4/PD-1 combination therapy and in anti-PD-1 inhibitor-associated colitis. On the basis of our data, we successfully targeted this pathway in a patient with refractory ICI-colitis, using the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib.
Conclusions: Interferon gamma-producing CD8+ TRM cells are a pathological hallmark of ICI-colitis and a novel target for therapy.
Keywords: Checkpoint Colitis; Immunotherapy Colitis; Tofacitinib; Ulcerative Colitis.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures








Comment in
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis: Resident Memory Unleashed.Gastroenterology. 2021 Oct;161(4):1106-1108. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.07.007. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Gastroenterology. 2021. PMID: 34256056 No abstract available.
References
-
- Larkin J., Hodi F.S., Wolchok J.D. Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab or monotherapy in untreated melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1270–1271. - PubMed
Supplementary References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

