Alveolar Recruitment Maneuver Reduces Cerebral Oxygen Saturation and Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity in Patients During Carotid Endarterectomy
- PMID: 34148051
- PMCID: PMC8223757
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.930617
Alveolar Recruitment Maneuver Reduces Cerebral Oxygen Saturation and Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity in Patients During Carotid Endarterectomy
Abstract
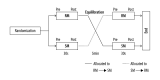
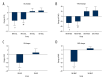
BACKGROUND This study aimed to determine the effects of alveolar recruitment maneuver (RM) on cerebral oxygen saturation and cerebral blood velocity in patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy (CEA) before clamping of the carotid artery. MATERIAL AND METHODS In this crossover exploratory study, all patients were randomized to undergo an RM (30 cmH₂O of continuous airway pressure for 30 s) and a "sham" maneuver (SM; 5 cmH₂O for 30 s), followed by an alternative intervention after a 5-min equilibration period. Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) was used to monitor regional cerebral oxygen saturation (rSO₂), and transcranial Doppler ultrasonography (TCD) to evaluate blood velocity of the middle cerebral artery (V-MCA). Changes in rSO₂, V-MCA, mean arterial pressure (MAP), and heart rate (HR) in response to the 2 interventions were compared. RESULTS A total of 59 patients underwent the study procedure. RM reduced rSO₂, V-MCA, MAP, and HR, but these variables slightly changed during SM. A significant drop in rSO₂ was observed immediately after RM compared with the baseline value (68.51±4.4% vs 64.12±5.15%; P<0.001). The decrease in rSO₂ was higher during the RM than during the SM (-6±4% vs 1±2%; P<0.001). Similarly, change in V-MCA was more significant in response to RM than SM (-26±19% vs 19±16%; P<0.001). The V-MCA value changed from 39 cm/s to 29 cm/s after RM. In addition, V-MCA of the ipsilateral to the surgical side decreased more obviously than the contralateral side (-26±19% vs -20±17%; P=0.001). CONCLUSIONS An RM at 30 cmH₂O of continuous airway pressure for 30 s decreased rSO₂ and V-MCA. In addition, MAP and HR were affected.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Efficacy of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Monitoring in Carotid Endarterectomy: A Prospective, Single-Center, Observational Study.Cell Transplant. 2019 Feb;28(2):170-175. doi: 10.1177/0963689718817760. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Cell Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30545240 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time continuous neuromonitoring combines transcranial cerebral Doppler with near-infrared spectroscopy cerebral oxygen saturation during total aortic arch replacement procedure: a pilot study.ASAIO J. 2012 Mar-Apr;58(2):122-6. doi: 10.1097/MAT.0b013e318241abd3. ASAIO J. 2012. PMID: 22370681
-
Near-infrared spectroscopy can predict the onset of cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome after carotid endarterectomy.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;34(4):314-21. doi: 10.1159/000343229. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012. PMID: 23146912
-
Transcranial Doppler ultrasound for cerebral perfusion.Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1995;625:1-44. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1995. PMID: 7484167 Review.
-
The value of near-infrared spectroscopy measured cerebral oximetry during carotid endarterectomy in perioperative stroke prevention. A review.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2009 Nov;38(5):539-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2009.07.008. Epub 2009 Aug 7. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2009. PMID: 19665397 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Manual Sustained Inflation vs Stepwise PEEP on Pulmonary and Cerebral Outcomes in Carotid Endarterectomy Patients.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Oct 8;30:e944936. doi: 10.12659/MSM.944936. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 39375912 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Howell SJ. Carotid endarterectomy. Brit J Anaesth. 2007;99:119–31. - PubMed
-
- Marinò V, Aloj F, Vargas M, et al. Intraoperative neurological monitoring with evoked potentials during carotid endarterectomy versus cooperative patients under general anesthesia technique. J Neurosurg Anesth. 2018;30:258–64. - PubMed
-
- Thirumala PD, Kumar H, Bertolet M, et al. Risk factors for cranial nerve deficits during carotid endarterectomy: A retrospective study. Clin Neurol Neurosur. 2015;130:150–54. - PubMed
-
- Kitagawa T, Ishikawa H, Yamamoto J, Ota S. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy and neurogenic pulmonary edema after carotid endarterectomy. World Neurosurg. 2019 [Online ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Ballotta E, Da GG, Renon L, et al. Cranial and cervical nerve injuries after carotid endarterectomy: A prospective study. Surgery. 1999;125:85–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

