Lamin post-translational modifications: emerging toggles of nuclear organization and function
- PMID: 34148760
- PMCID: PMC8793286
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.05.007
Lamin post-translational modifications: emerging toggles of nuclear organization and function
Abstract
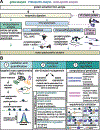
Nuclear lamins are ancient type V intermediate filaments with diverse functions that include maintaining nuclear shape, mechanosignaling, tethering and stabilizing chromatin, regulating gene expression, and contributing to cell cycle progression. Despite these numerous roles, an outstanding question has been how lamins are regulated. Accumulating work indicates that a range of lamin post-translational modifications (PTMs) control their functions both in homeostatic cells and in disease states such as progeria, muscular dystrophy, and viral infection. Here, we review the current knowledge of the diverse types of PTMs that regulate lamins in a site-specific manner. We highlight methods that can be used to characterize lamin PTMs whose functions are currently unknown and provide a perspective on the future of the lamin PTM field.
Keywords: PTMs; acetylation; farnesylation; lamins; phosphorylation; ubiquitination.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Lin F and Worman HJ (1995) Structural organization of the human gene (LMNB1) encoding nuclear lamin B1. Genomics 27, 230–236 - PubMed
-
- Lin F and Worman HJ (1993) Structural organization of the human gene encoding nuclear lamin A and nuclear lamin C. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 16321–16326 - PubMed
-
- McKeon FD et al. (1986) Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature 319, 463–468 - PubMed
-
- Broers JLV et al. (2006) Nuclear lamins: Laminopathies and their role in premature ageing. Physiol. Rev. 86, 967–1008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

