The Association between the Establishment of a General Internal Medicine Department and an Increased Number of Blood Cultures in Other Departments: An Interrupted Time Series Analysis
- PMID: 34148950
- PMCID: PMC8710379
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.6795-20
The Association between the Establishment of a General Internal Medicine Department and an Increased Number of Blood Cultures in Other Departments: An Interrupted Time Series Analysis
Abstract
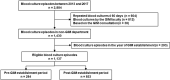
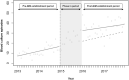
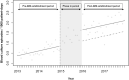
Objective The establishment of a department of general internal medicine (GIM) has been shown to improve the clinical outcomes among patients treated in GIM departments but the effect on practice patterns in other departments remains unclear. We evaluated the association between the establishment of a GIM department and the use of blood cultures, an indicator of quality of care of infectious diseases, in other departments. Methods This study was conducted between 2013 and 2017 in a community hospital which established a new GIM department in 2015, with a mandate to improve the quality of care of the hospital including infectious disease management. The primary outcome was the change in the number of blood culture episodes per calendar month in other departments before and after establishment of the GIM department. The secondary outcome was the change in the blood culture episodes per month, indexed to 1,000 patient-days, during the same time. Using 2015 as the phase-in period, interrupted time series analyses were used to evaluate the change in the outcome variables. Results In departments other than GIM, there were 284 blood cultures prior to the establishment of the GIM department (2013-2014) and 853 afterwards (2016-2017). The number of blood culture episodes in other departments increased by 10.7 (95%CI: 0.39-21.0, p=0.042) per calendar month after the establishment of the GIM department; blood culture episodes/calendar month/1,000 patient-days increased by 0.55 (95%CI: 0.03-1.07 p=0.037). Conclusion These results indicate that a GIM department in a community hospital can improve the quality of care in other departments.
Keywords: blood culture; general internal medicine; hospitalist; interrupted time series.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does Reducing Inpatient Length of Stay Have Upstream Effects on the Emergency Room: Exploring the Impact of the General Internal Medicine Care Transformation Initiative.Acad Emerg Med. 2016 Jun;23(6):711-7. doi: 10.1111/acem.12935. Epub 2016 May 11. Acad Emerg Med. 2016. PMID: 26850577
-
Survey of Inpatient Consultations with General Internal Medicine Physicians in a Tertiary Hospital: A Retrospective Observational Study.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Apr 14;16:1295-1302. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S408768. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37081930 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality of hospitalised internal medicine patients bedspaced to non-internal medicine inpatient units: retrospective cohort study.BMJ Qual Saf. 2018 Jan;27(1):11-20. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2017-006925. Epub 2017 Nov 3. BMJ Qual Saf. 2018. PMID: 29101293
-
The Evolution of General Internal Medicine (GIM)in Canada: International Implications.J Gen Intern Med. 2017 May;32(5):576-581. doi: 10.1007/s11606-016-3891-z. Epub 2016 Oct 24. J Gen Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 27778214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surgical treatment for urinary incontinence in women - Danish nationwide cohort studies .Dan Med J. 2018 Feb;65(2):B5447. Dan Med J. 2018. PMID: 29393041 Review.
Cited by
-
How Do We Establish the Utility and Evidence of General Medicine in Japan?Int J Gen Med. 2024 Feb 22;17:635-638. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S451260. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 38410241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The Japanese Society of Internal Medicine. Physicians of “general internists” and the appropriate number of the doctors [Internet]. Available from: https://www.naika.or.jp/nintei/seido/ishizo_top/ishizo_01/ (in Japanese)
-
- Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. Measures against uneven distribution of physicians [Internet]. Available from: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/file/06-Seisakujouhou-10800000-Iseikyoku/00001943... (in Japanese)
-
- American College of Physicians. About Internal Medicine [Internet]. Available from: https://www.acponline.org/about-acp/about-internal-medicine
-
- Iwata K. Quantitative and qualitative problems of infectious diseases fellowship in Japan. Int J Infect Dis 17: e1098-e1099, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Wada M, Nishiyama D, Kawashima A, Fujiwara M, Kagawa K. Effects of establishing a department of general internal medicine on the length of hospitalization. Intern Med 54: 2161-2165, 2015. - PubMed

