Comparative effects of quercetin, luteolin, apigenin and their related polyphenols on uric acid production in cultured hepatocytes and suppression of purine bodies-induced hyperuricemia by rutin in mice
- PMID: 34149170
- PMCID: PMC8167080
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-021-00452-9
Comparative effects of quercetin, luteolin, apigenin and their related polyphenols on uric acid production in cultured hepatocytes and suppression of purine bodies-induced hyperuricemia by rutin in mice
Abstract
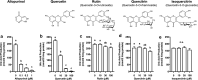
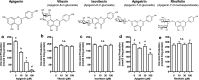
Hyperuricemia, the high uric acid (UA) state in blood, has been accepted as an important risk factor for gout. The liver is a main factory of UA production. In the present study, we have examined the effects of three kinds of flavonol and flavones as typical aglycons, i.e., quercetin, luteolin, apigenin, their glycosides and related compounds, on UA productivity in cultured hepatocytes, adopting allopurinol as the positive control drug. Quercetin, luteolin, diosmetin (4'-O-methylluteolin) and apigenin at 10, 30 and 100 μM as well as allopurinol at 0.1, 0.3 and 1 μM dose-dependently and significantly decreased UA production in the hepatocytes, when compared with 0 μM (control). Both rutin (quercetin-3-O-rutinoside) and quercitrin (quercetin-3-O-ramnoside) significantly reduced UA production in the hepatocytes at 100 μM. Luteolin glycosides such as orientin (luteolin-8-C-glucoside) and isoorientin (luteolin-6-C-glucoside) exerted no influences on it even at 100 μM. Likewise, apigenin glycosides such as vitexin (apigenin-8-C-glucoside) and isovitexin (apigenin-6-C-glucoside) showed no inhibitory effect on it, while apigetrin (apigenin-7-O-glucoside) significantly reduced it at 100 μM. In model mice with purine bodies-induced hyperuricemia, allopurinol completely suppressed the hyperuricemia at a dose of 10 mg/kg body weight. Rutin suppressed significantly the hyperuricemia at a dose of 300 mg/kg body weight, while vitexin showed no significant effect up to 300 mg/kg body weight. Thus, rutin (O-glycoside) is demonstrated to be hypouricemic in both cultured hepatocytes and model mice with recently contrived purine bodies-induced hyperuricemia.
Keywords: AML12 hepatocytes; Hyperuricemia; Purine body; Quercetin; Rutin; Uric acid.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThis study was funded by Suntory Malting Ltd., Utsunomiya, Tochigi, Japan. MO is the employee for this company.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Assay systems for screening food and natural substances that have anti-hyperuricemic activity: uric acid production in cultured hepatocytes and purine bodies-induced hyperuricemic model mice.Cytotechnology. 2017 Jun;69(3):435-442. doi: 10.1007/s10616-016-0005-z. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Cytotechnology. 2017. PMID: 27518104 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-hyperuricemic effect of isorhamnetin in cultured hepatocytes and model mice: structure-activity relationships of methylquercetins as inhibitors of uric acid production.Cytotechnology. 2019 Feb;71(1):181-192. doi: 10.1007/s10616-018-0275-8. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Cytotechnology. 2019. PMID: 30603920 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction optimization, structural characterization and potential alleviation of hyperuricemia by flavone glycosides from celery seeds.Food Funct. 2022 Oct 3;13(19):9832-9846. doi: 10.1039/d2fo01715f. Food Funct. 2022. PMID: 36047466
-
Exploring natural products-based cancer therapeutics derived from egyptian flora.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113626. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113626. Epub 2020 Nov 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33248183 Review.
-
A review on the fruit components affecting uric acid level and their underlying mechanisms.J Food Biochem. 2021 Oct;45(10):e13911. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13911. Epub 2021 Aug 23. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34426969 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating natural products with modern medicine in the treatment of gouty arthritis: a review.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 May 26. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01784-0. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40418438 Review.
-
Protective Effects of a Polyherbal Mixture on Intestinal Injury via the NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Gut Microbiota Modulation in Hyperuricemic Mice.Foods. 2025 Mar 24;14(7):1118. doi: 10.3390/foods14071118. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40238278 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Hypouricemic Effect of Bioactive Compounds: Molecular Evidence and Potential Application in the Management of Gout.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Oct 25;44(11):5173-5190. doi: 10.3390/cimb44110352. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36354664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apigenin Ameliorates Hyperuricemia and Renal Injury through Regulation of Uric Acid Metabolism and JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;15(11):1442. doi: 10.3390/ph15111442. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36422572 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Hydroxyethyl Starch Luteolin Nanocrystals for Effective Anti-Hyperuricemia Effect in Mice Model.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jun 4;19:5139-5156. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S464948. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38859954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi SI, Yoshizawa F, Yagasaki K. Assay systems for screening food and natural substances that have anti-hyperuricemic activity: uric acid production in cultured hepatocytes and purine bodies-induced hyperuricemic model mice. Cytotechnology. 2017;69:435–442. doi: 10.1007/s10616-016-0005-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adachi SI, Kondo S, Sato Y, Yoshizawa F, Yagasaki K. Anti-hyperuricemic effect of isorhamnetin in cultured hepatocytes and model mice: structure-activity relationships of methylquercetins as inhibitors of uric acid production. Cytotechnology. 2019;71:181–192. doi: 10.1007/s10616-018-0275-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

