Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Super-Refractory Status Epilepticus at a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: A Single-Center Experience
- PMID: 34149600
- PMCID: PMC8209375
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.669296
Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Super-Refractory Status Epilepticus at a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
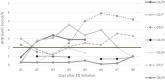
Background: To evaluate the use of the ketogenic diet (KD) for treatment of super-refractory status epilepticus (SRSE) at a pediatric intensive care unit (PICU). Design: A retrospective analysis of all pediatric patients treated for SRSE with the KD at our center was performed using patient data from our prospective longitudinal KD database. Setting: SRSE is defined as refractory SE that continues or recurs 24 h or more after initiation of anesthetic drugs. We describe the clinical and electroencephalographic (EEG) findings of all children treated with KD at our PICU. The KD was administered as add-on after failure of standard treatment. Response was defined as EEG seizure resolution (absence of seizures and suppression-burst ratio ≥50%). Patients: Eight consecutive SRSE patients (four females) treated with KD were included. Median age at onset of SRSE was 13.6 months (IQR 0.9-105), and median age at KD initiation was 13.7 months (IQR 1.9 months to 8.9 years). Etiology was known in 6/8 (75%): genetic in 4 (50%), structural in 1 (12.5%), and autoimmune/inflammatory in 1 (12.5%). Main Results: Time from onset of SRSE to initiation of KD was median 6 days (IQR 1.3-9). Time until clinically relevant ketosis (beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) >2 mmol/L in serum) was median 68.0 h (IQR 27.3-220.5). Higher ketosis was achieved when a higher proportion of enteral feeds was possible. Four (50%) patients responded to KD treatment within 7 days. During follow-up (median 4.2 months, IQR 1.6-12.3), 5/8 patients-three of them responders-died within 3-12 months after SRSE. Conclusions: In eight patients with SRSE due to severe etiologies including Alpers syndrome, we report an initial 50% response to KD. KD was used early in SRSE and sufficient levels of ketosis were reached early in most patients. Higher ketosis was achieved with combined enteral and parenteral feedings.
Keywords: beta-hydroxybutyrate; ketogenic diet; parenteral diet; pediatric; status epilepticus.
Copyright © 2021 Breu, Häfele, Glatter, Trimmel-Schwahofer, Golej, Male, Feucht and Dressler.
Conflict of interest statement
AD has received travel reimbursement and speaker honoraria from SHS, Nutricia and Vitaflo. PT-S has received travel reimbursement from SHS, Nutricia and Vitaflo. MF received travel reimbursement from SHS, Nutricia. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes of parenteral vs enteral ketogenic diet in pediatric super-refractory status epilepticus.Seizure. 2022 Mar;96:79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2022.01.019. Epub 2022 Feb 5. Seizure. 2022. PMID: 35158320
-
A Practical Approach to Ketogenic Diet in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit for Super-Refractory Status Epilepticus.Neurocrit Care. 2017 Apr;26(2):267-272. doi: 10.1007/s12028-016-0312-4. Neurocrit Care. 2017. PMID: 27553113
-
Ketogenic diet for adults in super-refractory status epilepticus.Neurology. 2014 Feb 25;82(8):665-70. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000151. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24453083 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Management of Children With Super-Refractory Status Epilepticus: A Systematic Review and Experience in a Single UK Tertiary Centre.Front Neurol. 2021 Mar 12;12:643105. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.643105. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33776895 Free PMC article.
-
Medium-chain triglyceride ketogenic diet is effective for treatment of an adult with super-refractory status epilepticus: a case report and literature review.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019 Dec;73(12):1594-1597. doi: 10.1038/s41430-019-0471-4. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31316173 Review.
Cited by
-
Ketogenic diet treatment for super-refractory status epilepticus in the intensive care unit: feasibility, safety and effectiveness.Front Neurol. 2025 Jan 13;15:1517850. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1517850. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39871989 Free PMC article.
-
Ketogenic diet for super-refractory status epilepticus (SRSE) with NORSE and FIRES: Single tertiary center experience and literature data.Front Neurol. 2023 Apr 13;14:1134827. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1134827. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37122314 Free PMC article.
-
Kenyan dietitians' knowledge of ketogenic dietary therapies for drug-resistant epilepsy.BMC Nutr. 2025 Aug 2;11(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s40795-025-01144-9. BMC Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40753441 Free PMC article.
-
Favorable response to classic ketogenic diet in a child with anti-GAD 65 antibody mediated super refractory status epilepticus.Epilepsy Behav Rep. 2022 Jun 7;19:100557. doi: 10.1016/j.ebr.2022.100557. eCollection 2022. Epilepsy Behav Rep. 2022. PMID: 35789965 Free PMC article.
-
Ketogenic dietary therapy utilization in Kenya: A qualitative exploration of dietitian's perceptions.Epilepsy Behav Rep. 2024 Mar 20;26:100661. doi: 10.1016/j.ebr.2024.100661. eCollection 2024. Epilepsy Behav Rep. 2024. PMID: 38560597 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

