Unraveling the Novel Effect of Patchouli Alcohol Against the Antibiotic Resistance of Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 34149664
- PMCID: PMC8206506
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.674560
Unraveling the Novel Effect of Patchouli Alcohol Against the Antibiotic Resistance of Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
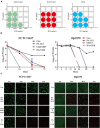
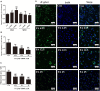
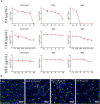
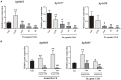
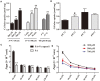
The long-term colonization of Helicobacter pylori can cause various gastrointestinal diseases, and its high genetic variability is prone to antibiotic resistance and leads to failure of clinical treatment. Intracellular survival also contributes to the drug tolerance of H. pylori. Patchouli alcohol (PA) shows a highly efficient activity against H. pylori in vitro and in vivo. And this study aims to explore whether PA can reduce the resistance of H. pylori and determine the underlying mechanism. Checkerboard and time-kill bactericidal curve assay reveal that the combination of PA and clarithromycin (CLR) promoted the inhibition and bactericidal effect against H. pylori. Stimulation of CLR leads to the internalization of H. pylori, but PA can effectively inhibit the invasion induced by CLR. Compared with antibiotics, PA remarkably eradicated the intracellular H. pylori, and this intracellular sterilized ability was further improved in combination with antibiotics (CLR and metronidazole). The expression of H. pylori efflux pump genes (hp0605, hp1327, and hp1489) was dose-dependently downregulated by PA. Digital droplet PCR indicated that the H. pylori mutant of A2143G can be inhibited by PA. Cellular uptake and transport assays showed that PA is rapidly absorbed, which promotes its activity against intracellular bacteria. Therefore, PA can act synergistically with CLR as a candidate treatment against drug-resistant H. pylori.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; clarithromycin; intracellular; patchouli alcohol; resistance.
Copyright © 2021 Zhong, Tang, Deng, Jing, Zhang, Zhang, Yu, Ou, Guo, Huang, Cao, Huang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Antibacterial Activities of Patchouli Alcohol, a Naturally Occurring Tricyclic Sesquiterpene, against Helicobacter pylori Infection.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 May 24;61(6):e00122-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00122-17. Print 2017 Jun. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28320722 Free PMC article.
-
Application of next-generation sequencing to characterize novel mutations in clarithromycin-susceptible Helicobacter pylori strains with A2143G of 23S rRNA gene.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2018 Mar 22;17(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12941-018-0259-8. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2018. PMID: 29562911 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Novel Protective Effect of Patchouli Alcohol Against Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastritis: Insights Into the Molecular Mechanism in vitro and in vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 22;9:1347. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01347. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30524287 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of clarithromycin-resistant Helicobacter pylori in clinical specimens by molecular methods: A review.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2016 Mar;4:35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2016.01.002. Epub 2016 Feb 8. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2016. PMID: 27436390 Review.
-
Novel and Effective Therapeutic Regimens for Helicobacter pylori in an Era of Increasing Antibiotic Resistance.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 May 5;7:168. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00168. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28529929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Patchouli alcohol induces G0 /G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in vincristine-resistant non-small cell lung cancer through ROS-mediated DNA damage.Thorac Cancer. 2023 Jul;14(21):2007-2017. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14982. Epub 2023 May 30. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37249164 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Drug Delivery Systems for Combating H. pylori: A Brief Review.Arch Razi Inst. 2024 Oct 31;79(5):903-914. doi: 10.32592/ARI.2024.79.5.903. eCollection 2024 Oct. Arch Razi Inst. 2024. PMID: 40292064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory mechanism of the non-volatile ingredients originated from Guanghuoxiang () based on high performance liquid chromatography-heated electron spray ionization-high resolution mass spectroscope and cell metabolomics.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Apr;44(2):260-267. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240203.003. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38504532 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Coculture Model for Assessing Competing Host Mammalian Cell and Bacterial Attachment on Zirconia versus Titanium.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024 Oct 14;10(10):6218-6229. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.4c01075. Epub 2024 Sep 23. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024. PMID: 39312708
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Effect of Amikacin and Imipenem Combinations against Multidrug-Resistant E. coli.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022 Oct 2;7(10):281. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed7100281. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36288022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alba C., Blanco A., Alarcon T. (2017). Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 30 489–497. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

