Rodent Models of Spondyloarthritis Have Decreased White and Bone Marrow Adipose Tissue Depots
- PMID: 34149700
- PMCID: PMC8207134
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.665208
Rodent Models of Spondyloarthritis Have Decreased White and Bone Marrow Adipose Tissue Depots
Abstract
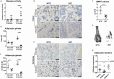
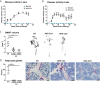
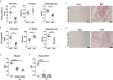
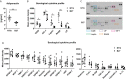
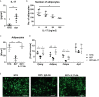
Bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT) has recently been recognized as a distinct fat depot with endocrine functions. However, if and how it is regulated by chronic inflammation remains unknown. Here, we investigate the amount of white fat and BMAT in HLA-B27 transgenic rats and curdlan-challenged SKG mice, two well-established models of chronic inflammatory spondyloarthritis (SpA). Subcutaneous and gonadal white adipose tissue and BMAT was reduced by 65-70% and by up to 90% in both experimental models. Consistently, B27 rats had a 2-3-fold decrease in the serum concentrations of the adipocyte-derived cytokines adiponectin and leptin as well as a 2-fold lower concentration of triglycerides. The bone marrow of B27 rats was further characterized by higher numbers of neutrophils, lower numbers of erythroblast precursors, and higher numbers of IL-17 producing CD4+ T cells. IL-17 concentration was also increased in the serum of B27 rats. Using a cell culture model, we show that high levels of IL-17 in the serum of B27 rats negatively impacted adipogenesis (-76%), an effect that was reversed in the presence of neutralizing anti-IL-17 antibody. In summary, these findings show BMAT is severely reduced in two experimental models of chronic inflammatory SpA and suggest that IL-17 is involved in this process.
Keywords: HLA-B27 transgenic rat; IL-17; SKG mouse; bone marrow fat; spondyloarthritis.
Copyright © 2021 Furesi, Fert, Beaufrère, Araujo, Glatigny, Baschant, von Bonin, Hofbauer, Horwood, Breban and Rauner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

