Type I Interferon Dependent hsa-miR-145-5p Downregulation Modulates MUC1 and TLR4 Overexpression in Salivary Glands From Sjögren's Syndrome Patients
- PMID: 34149728
- PMCID: PMC8208490
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.685837
Type I Interferon Dependent hsa-miR-145-5p Downregulation Modulates MUC1 and TLR4 Overexpression in Salivary Glands From Sjögren's Syndrome Patients
Abstract
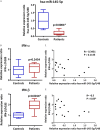
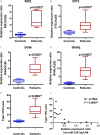
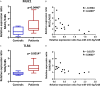
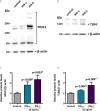
Sjögren's syndrome (SS) is an autoimmune disease that mainly affects salivary glands (SG) and is characterized by overactivation of the type I interferon (IFN) pathway. Type I IFNs can decrease the levels of hsa-miR-145-5p, a miRNA with anti-inflammatory roles that is downregulated in SG from SS-patients. Two relevant targets of hsa-miR-145-5p, mucin 1 (MUC1) and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) are overexpressed in SS-patients and contribute to SG inflammation and dysfunction. This study aimed to evaluate if hsa-miR-145-5p modulates MUC1 and TLR4 overexpression in SG from SS-patients in a type I IFN dependent manner. Labial SG (LSG) biopsies from 9 SS-patients and 6 controls were analyzed. We determined hsa-miR-145-5p levels by TaqMan assays and the mRNA levels of MUC1, TLR4, IFN-α, IFN-β, and IFN-stimulated genes (MX1, IFIT1, IFI44, and IFI44L) by real time-PCR. We also performed in vitro assays using type I IFNs and chemically synthesized hsa-miR-145-5p mimics and inhibitors. We validated the decreased hsa-miR-145-5p levels in LSG from SS-patients, which inversely correlated with the type I IFN score, mRNA levels of IFN-β, MUC1, TLR4, and clinical parameters of SS-patients (Ro/La autoantibodies and focus score). IFN-α or IFN-β stimulation downregulated hsa-miR-145-5p and increased MUC1 and TLR4 mRNA levels. Hsa-miR-145-5p overexpression decreased MUC1 and TLR4 mRNA levels, while transfection with a hsa-miR-145-5p inhibitor increased mRNA levels. Our findings show that type I IFNs decrease hsa-miR-145-5p expression leading to upregulation of MUC1 and TLR4. Together, this suggests that type I interferon-dependent hsa-miR-145-5p downregulation contributes to the perpetuation of inflammation in LSG from SS-patients.
Keywords: Mucin 1; Sjögren’s syndrome; Toll-like receptor 4; Type I interferons; hsa-miR-145-5p.
Copyright © 2021 Jara, Carvajal, Castro, Barrera, Aguilera, González, Molina, Hermoso and González.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integrated stress response inhibition restores hsa-miR-145-5p levels after IFN-β stimulation in salivary gland epithelial cells. Association between cellular stress and miRNA biogenesis in Sjögren's disease.J Autoimmun. 2025 May;153:103412. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2025.103412. Epub 2025 Apr 1. J Autoimmun. 2025. PMID: 40174282
-
hsa-miR-424-5p and hsa-miR-513c-3p dysregulation mediated by IFN-γ is associated with salivary gland dysfunction in Sjögren's syndrome patients.J Autoimmun. 2023 Jul;138:103037. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103037. Epub 2023 May 23. J Autoimmun. 2023. PMID: 37229808
-
Small RNA Expression Profiling Reveals hsa-miR-181d-5p Downregulation Associated With TNF-α Overexpression in Sjögren's Syndrome Patients.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 1;13:870094. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.870094. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35432384 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the type I interferon pathway in primary Sjogren's syndrome.J Autoimmun. 2010 Nov;35(3):225-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2010.06.012. Epub 2010 Jul 31. J Autoimmun. 2010. PMID: 20674271 Review.
-
The Role of Interferons in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren's Syndrome and Future Therapeutic Perspectives.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 9;11(2):251. doi: 10.3390/biom11020251. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33572487 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Explore the possible influence of Sjogren's syndrome on thyroid cancer: A literature data mining and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 10;20(2):e0318747. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318747. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39928612 Free PMC article.
-
View from the Biological Property: Insight into the Functional Diversity and Complexity of the Gut Mucus.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 20;24(4):4227. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044227. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic impact of MUC1 and potential regulatory miR-145 and miR-21 expression in salivary mucoepidermoid carcinoma.Head Neck Pathol. 2022 Dec;16(4):1134-1145. doi: 10.1007/s12105-022-01475-0. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Head Neck Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35980523 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of tricellular tight junction tricellulin leads to hyposalivation in Sjögren's syndrome.Int J Oral Sci. 2025 Mar 19;17(1):22. doi: 10.1038/s41368-025-00349-9. Int J Oral Sci. 2025. PMID: 40108118 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering potential new biomarkers and immune infiltration characteristics in primary Sjögren's syndrome by integrated bioinformatics analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 13;102(41):e35534. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035534. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37832090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fox RI, Kang HI, Ando D, Abrams J, Pisa E. Cytokine mRNA Expression in Salivary Gland Biopsies of Sjögren’s Syndrome. J Immunol (1994) 152(11):5532–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

