Bacteriocin activity of various iranian honey-associated bacteria and development of a simple medium for enhanced bacteriocin activity
- PMID: 34150246
- PMCID: PMC8172756
- DOI: 10.1007/s40201-021-00615-y
Bacteriocin activity of various iranian honey-associated bacteria and development of a simple medium for enhanced bacteriocin activity
Abstract
Purpose: Honey is a promising source of bacterial strains producing metabolites with antimicrobial activity. There is a great variety in the antimicrobial activity of honey from different areas of nature. Therefore, the aim of present study was to investigate the antibacterial activity of Iranian honey from different regions and to optimize the culture condition for the highly potent bacterial isolate.
Methods: Honey samples were collected from ten different regions of Iran and were screened for bacteriocin-producing bacteria. The best bacteriocin-producing strain was characterized and identified by 16S rDNA analysis. One-factor-at-a-time method was used for optimization of culture medium and the yield and time-course of bacteriocin production were compared in both shake flask and bio-reactor.
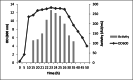
Results: The Bacillus subtilis SB1 that was isolated from Sabalan honey showed potent antibacterial activity with prominent thermal stability. The optimum medium for the bacteiocin production was a yeast extract-based medium. The optimum incubation temperature for bacteriocin production was 34 °C. Bacteriocin production was higher near neutral pH conditions than that produced at acidic or alkaline environment. The results of cell growth and bacteriocin assays revealed that the exponential phase of growth and antibacterial compounds production was started rapidly in bioreactor than flask.
Conclusions: Findings of this study supported the folkloric application of honey against some infectious diseases. B.subtilis SB1 that isolated from Sabalan honey was a potential source for bacteriocins-like compounds. Our studies suggested a simple buffered nitrogen-based medium for SB1 growth and bacteriocin activity in both shake flask and bioreactor.
Keywords: Antibacterial activity; Bacillus subtilis; Bacteriocin; Honey.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bacteriocin (BAC-IB17): screening, isolation and production from Bacillus subtilis KIBGE IB-17.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2012 Jan;25(1):195-201. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2012. PMID: 22186330
-
Optimization of Culture Conditions and Batch Process Control for the Augmented Production of Bacteriocin by Bacillus Species.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 25;12(4):651. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040651. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674596 Free PMC article.
-
Partial characterization of bacteriocin-like compounds from two strains of Bacillus cereus with biological activity against Paenibacillus larvae, the causal agent of American Foulbrood disease.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016 Dec;63(6):442-449. doi: 10.1111/lam.12665. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27589675
-
Growth Optimization of Lactobacillus acidophilus for Production of Antimicrobial Peptide Acidocin 4356: Scale up from Flask to Lab-Scale Fermenter.Iran J Biotechnol. 2021 Jul 1;19(3):e2686. doi: 10.30498/ijb.2021.218725.2686. eCollection 2021 Jul. Iran J Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34825011 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Potency of Honey.Int J Microbiol. 2019 Jun 2;2019:2464507. doi: 10.1155/2019/2464507. eCollection 2019. Int J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31281362 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bee Pollen and Bee Bread as a Source of Bacteria Producing Antimicrobials.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Jun 13;10(6):713. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10060713. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34199247 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication and antimicrobial properties of novel meropenem-honey encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles against multiresistant and biofilm-forming Staphylococcus aureus as a new antimicrobial agent.Vet Med Sci. 2024 May;10(3):e1440. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1440. Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38613443 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the microbiome in Apis cerana honey highlights honey as a potential source for the isolation of beneficial bacterial strains.PeerJ. 2024 Mar 27;12:e17157. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17157. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38560453 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of different growth conditions of Bacillus subtilis isolated from membrane-less microbial fuel cell toward antimicrobial activity profiling.Open Life Sci. 2024 Jan 24;19(1):20220809. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0809. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38283116 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases