Investigating the Effect of Near Infra-Red Spectroscopy (NIRS) on Early Diagnosis of Cardiac Surgery-Associated Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 34150576
- PMCID: PMC8207845
- DOI: 10.5812/aapm.109863
Investigating the Effect of Near Infra-Red Spectroscopy (NIRS) on Early Diagnosis of Cardiac Surgery-Associated Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
Background: Cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury (CSA-AKI) is a major adverse effect of cardiac surgery. The early detection of this complication can improve the quality of postoperative care and help prevent this phenomenon.
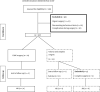
Methods: In this prospective descriptive-analytical study, 148 patients were enrolled, 107 of whom were selected for analysis between February and September 2019 in the Cardiac Surgery Unit of Golestan Hospital, Ahvaz, Iran. Kidney tissue oxygen saturation was measured at multiple definite times during surgery. Hemoglobin, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, and lactate were measured during and 48 hours after the surgery.
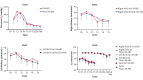
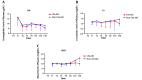
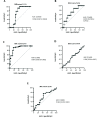
Results: Forty-one patients were diagnosed with CSA-AKI according to the KDIGO criteria. Parametric and non-parametric analyses showed no significant difference between the CSA-AKI and non-CSA-AKI groups in the demographic parameters. Repeated measures ANOVA showed no significant difference in parameters, except for BUN. Repeated measures ANOVA showed a significant difference between both groups and time factors (P < 0.001, P = 0.0006, respectively). The ROC curve analyses showed that in a single point of time, the difference in the middle of CPB time from baseline had a high value in the prediction of AKI (AUC: 0.764; CI: 0.57 - 0.951).
Conclusions: Kidney saturation monitoring could be considered in cardiac surgery for the rapid detection of CSA-AKI. Although kidney tissue saturation is not correlated directly to the arterial oxygen saturation, the physician and the surgery team can predict the chance of acute kidney injury.
Keywords: Acute Kidney Injury; Cardiac Surgery; Near Infra-Red Spectroscopy.
Copyright © 2020, Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests: There is no conflict of interest to be declared.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources