Angiectatic Sinonasal Polyp: A Diagnostic Challenge
- PMID: 34150602
- PMCID: PMC8163935
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-020-02125-z
Angiectatic Sinonasal Polyp: A Diagnostic Challenge
Abstract
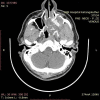
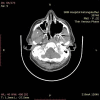
Sinonasal angiectatic polyp is an uncommon condition with features that masquerade various pathologies like hemangioma, angiofibroma, inverted papilloma, malignancy. We report a case of a left-sided vascular nasal mass, which on examination and investigations suggested cavernous hemangioma of the left maxillary sinus, whereas histopathology post-excision revealed angiectatic polyp.
Keywords: Angiectatic polyp; Double approach; Endoscopic excision; Hemangioma.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestDr. P.K. Purushothaman, Dr. Sharanya M, Dr. Manoj Pandian SP declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jayaram S, Svecova N, Biggs T, Theaker J, Salib RJ. Angiectatic nasal polyp: the great imitator? Int J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;15:1–3.
-
- Bhama L, Soni N. Angiomatous antrochoanal polyp causing epistaxis and bone destruction. Int J Clin Rhinol. 2018;11:25–28. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1338. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
