The Human Gut Phageome: Origins and Roles in the Human Gut Microbiome
- PMID: 34150671
- PMCID: PMC8213399
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.643214
The Human Gut Phageome: Origins and Roles in the Human Gut Microbiome
Abstract
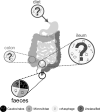
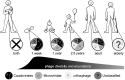
The investigation of the microbial populations of the human body, known as the microbiome, has led to a revolutionary field of science, and understanding of its impacts on human development and health. The majority of microbiome research to date has focussed on bacteria and other kingdoms of life, such as fungi. Trailing behind these is the interrogation of the gut viruses, specifically the phageome. Bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacterial hosts, are known to dictate the dynamics and diversity of bacterial populations in a number of ecosystems. However, the phageome of the human gut, while of apparent importance, remains an area of many unknowns. In this paper we discuss the role of bacteriophages within the human gut microbiome. We examine the methods used to study bacteriophage populations, how this evolved over time and what we now understand about the phageome. We review the phageome development in infancy, and factors that may influence phage populations in adult life. The role and action of the phageome is then discussed at both a biological-level, and in the broader context of human health and disease.
Keywords: bacteriophages; biofilm; diet; disease; gut microbiome; isolation; metagenomics; phage.
Copyright © 2021 Townsend, Kelly, Muscatt, Box, Hargraves, Lilley and Jameson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Akçelik M. (1998). A Phage DNA Injection-Blocking Type Resistance Mechanism Encoded by Chromosomal DNA in Lactococcus Lactis Subsp. Lactis PLM-18. Milchwissenschaft 53, 619–622.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

