N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Inflammation: Roles, Mechanisms, and Applications
- PMID: 34150765
- PMCID: PMC8213350
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.670711
N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Inflammation: Roles, Mechanisms, and Applications
Abstract
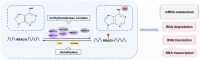
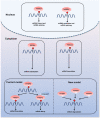
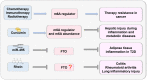
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent internal mRNA modification. m6A can be installed by the methyltransferase complex and removed by demethylases, which are involved in regulating post-transcriptional expression of target genes. RNA methylation is linked to various inflammatory states, including autoimmunity, infection, metabolic disease, cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, heart diseases, and bone diseases. However, systematic knowledge of the relationship between m6A modification and inflammation in human diseases remains unclear. In this review, we will discuss the association between m6A modification and inflammatory response in diseases, especially the role, mechanisms, and potential clinical application of m6A as a biomarker and therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; RNA modification; epigenetics; inflammation; inflammatory disease.
Copyright © 2021 Luo, Xu and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation and skin diseases.Autoimmunity. 2023 Dec;56(1):2167983. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2023.2167983. Autoimmunity. 2023. PMID: 36708146 Review.
-
The emerging roles of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) deregulation in liver carcinogenesis.Mol Cancer. 2020 Feb 28;19(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01172-y. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32111216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of N6-methyladenosine and its role in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2019 Dec 4;18(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1109-9. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31801551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of N6-methyladenosine with viruses and related diseases.Virol J. 2019 Nov 11;16(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1236-3. Virol J. 2019. PMID: 31711514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Insights Into the Role of N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Bone Pathophysiology.Stem Cells Dev. 2021 Jan 1;30(1):17-28. doi: 10.1089/scd.2020.0157. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Stem Cells Dev. 2021. PMID: 33231507 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of m6A Modification and m6A Regulators in Esophageal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 20;14(20):5139. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205139. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Epigenetics of the immune component of inflammation.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 22;13:1000836. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1000836. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36072580 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Promotion of the resistance of human oral epithelial cells to herpes simplex virus type I infection via N6-methyladenosine modification.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Feb 23;23(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-02744-2. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 36814204 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional control of haemostatic genes: mechanisms and emerging therapeutic concepts in thrombo-inflammatory disorders.Cardiovasc Res. 2023 Jul 6;119(8):1624-1640. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvad046. Cardiovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 36943786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL14 is Involved in TNF-α-Induced Inflammation in Colorectal Epithelial Cells via Autophagy Modulation.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;196(12):8453-8470. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-04940-4. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38878159
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

