Stabilization of an 211At-Labeled Antibody with Sodium Ascorbate
- PMID: 34151070
- PMCID: PMC8209801
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00684
Stabilization of an 211At-Labeled Antibody with Sodium Ascorbate
Abstract
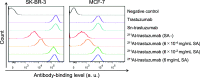
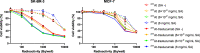
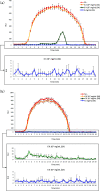
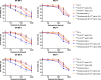
211At, an α-particle emitter, has recently attracted attention for radioimmunotherapy of intractable cancers. However, our sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and flow cytometry analyses revealed that 211At-labeled immunoconjugates are easily disrupted. Luminol assay revealed that reactive oxygen species generated from radiolysis of water caused the disruption of 211At-labeled immunoconjugates. To retain their functions, we explored methods to protect 211At-immunoconjugates from oxidation and enhance their stability. Among several other reducing agents, sodium ascorbate most safely and successfully protected 211At-labeled trastuzumab from oxidative stress and retained the stability of the 211At-labeled antibody and its cytotoxicity against antigen-expressing cells for several days.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Dekempeneer Y.; Keyaerts M.; Krasniqi A.; Puttemans J.; Muyldermans S.; Lahoutte T.; D’huyvetter M.; Devoogdt N. Targeted alpha therapy using short-lived alpha-particles and the promise of nanobodies as targeting vehicle. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 1035–1047. 10.1080/14712598.2016.1185412. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

