Deferoxamine-Modified Hybrid Materials for Direct Chelation of Fe(III) Ions from Aqueous Solutions and Indication of the Competitiveness of In Vitro Complexing toward a Biological System
- PMID: 34151096
- PMCID: PMC8210399
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01411
Deferoxamine-Modified Hybrid Materials for Direct Chelation of Fe(III) Ions from Aqueous Solutions and Indication of the Competitiveness of In Vitro Complexing toward a Biological System
Abstract
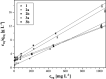
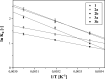
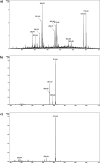
Deferoxamine (DFO) is one of the most potent iron ion complexing agent belonging to a class of trihydroxamic acids. The extremely high stability constant of the DFO-Fe complex (log β = 30.6) prompts the use of deferoxamine as a targeted receptor for scavenging Fe(III) ions. The following study aimed at deferoxamine immobilization on three different supports: poly(methyl vinyl ether-alt-maleic anhydride), silica particles, and magnetite nanoparticles, leading to a class of hybrid materials exhibiting effectiveness in ferric ion adsorption. The formed deferoxamine-loaded hybrid materials were characterized with several analytical techniques. Their adsorptive properties toward Fe(III) ions in aqueous samples, including pH-dependence, isothermal, kinetic, and thermodynamic experiments, were investigated. The materials were described with high values of maximal adsorption capacity q m, which varied between 87.41 and 140.65 mg g-1, indicating the high adsorptive potential of the DFO-functionalized materials. The adsorption processes were also described as intense, endothermic, and spontaneous. Moreover, an exemplary magnetically active deferoxamine-modified material has been proven for competitive in vitro binding of ferric ions from the biological complex protoporphyrin IX-Fe(III), which may lead to a further examination of the materials' biological or medical applicability.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Lane D. J.; Mills T. M.; Shafie N. H.; Merlot A. M.; Moussa R. S.; Kalinowski D. S.; Kovacevic Z.; Pichardson D. R. Expanding horizons in iron chelation and the treatment of cancer: role of iron in the regulation of ER stress and the epithelial – mesenchymal transition. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1845, 166–181. 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.01.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cozar O.; Leopold N.; Jelic C.; Chis V.; David L.; Mocanu A.; Tomoaia–Cotis M. IR, Raman and surface–enhanced Raman study of desferrioxamine B and its Fe(III) complex, ferrioxamine B. J. Mol. Structure 2006, 788, 1–6. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2005.04.035. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

