Using the dCas9-KRAB system to repress gene expression in hiPSC-derived NGN2 neurons
- PMID: 34151300
- PMCID: PMC8188621
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100580
Using the dCas9-KRAB system to repress gene expression in hiPSC-derived NGN2 neurons
Abstract
We describe a CRISPR inhibition (CRISPRi) protocol to repress endogenous gene expression (e.g., ATP6V1A) in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived NGN2-induced glutamatergic neurons. CRISPRi enables efficient and precise gene repression of one or multiple target genes via delivering gRNA(s) to direct a dCas9-KRAB fusion protein to the gene(s) of interest. This protocol can also be adapted for gene activation and high-throughput gene manipulation, allowing assessment of the transcriptomic and phenotypic impact of candidate gene(s) associated with neurodevelopment or brain disease. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Ho et al. (2017) and Wang et al. (2021).
Keywords: CRISPR; Cell Differentiation; Molecular Biology; Neuroscience; Stem Cells.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



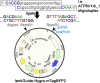




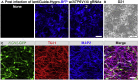

References
-
- Ho S.M., Hartley B.J., Flaherty E., Rajarajan P., Abdelaal R., Obiorah I., Barretto N., Muhammad H., Phatnani H.P., Akbarian S., Brennand K.J. Evaluating synthetic activation and repression of neuropsychiatric-related genes in hiPSC-derived NPCs, neurons, and astrocytes. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;9:615–628. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

