Combined detection of procalcitonin, heparin-binding protein, and interleukin-6 is a promising assay to diagnose and predict acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 34151489
- PMCID: PMC8373338
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23869
Combined detection of procalcitonin, heparin-binding protein, and interleukin-6 is a promising assay to diagnose and predict acute pancreatitis
Abstract
Background: Acute pancreatitis (AP), one of the most common clinical emergencies, is characterized by variable clinical features and inadequate diagnostic methods. At present, the commonly used indicators do not have high specificity and do not necessarily reflect disease severity. We therefore aimed to investigate diagnostic and prognostic value of plasma procalcitonin, heparin-binding protein, and interleukin-6 for acute pancreatitis by separate detection and joint detection.
Methods: The study involved 451 participants, including 343 AP patients and 108 healthy controls. We analyzed the association of the three biomarkers with the severity and prognosis of AP.
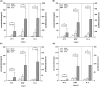
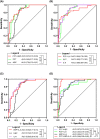
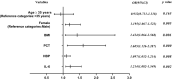
Results: A statistically significant increase in the mean plasma analyte levels was detected in the study group compared to the control group. Multivariate comparison showed that plasma levels of PCT, HBP, and IL-6 were all significantly different among the three groups at different sampling times (1st, 3rd, 7th, and 10th day of admission) (p < 0.01). The combination of the three indicators had significantly higher diagnostic value than either the individual markers or pairwise combinations (p < 0.001). The levels of the three were all significantly higher in severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) patients than in non-SAP patients (p < 0.001); meanwhile, patients with high levels had a worse prognosis than those with low levels (p < 0.05). In multivariate analysis adjusted for age and sex, high levels of PCT, HBP, and IL-6 were found to be independently associated with the development of AP.
Conclusions: It dramatically improved the diagnostic power of AP when PCT, HBP, and IL-6 were combined; high PCT, HBP, and IL-6 levels within 3 days of admission may be the potentially useful indicators for predicting SAP.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; diagnose; heparin-binding protein; interleukin-6; predict; procalcitonin.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic, monitoring, and prognostic value of combined detection of cerebrospinal fluid heparin-binding protein, interleukin-6, interleukin-10, and procalcitonin for post-neurosurgical intracranial infection.Cytokine. 2024 Jul;179:156593. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156593. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Cytokine. 2024. PMID: 38581866
-
Clinical significance of PCT, CRP, IL-6, NLR, and TyG Index in early diagnosis and severity assessment of acute pancreatitis: A retrospective analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 23;15(1):2924. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86664-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39849025 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-Binding Protein Levels at Admission and Within 24 h Are Associated with Persistent Organ Failure in Acute Pancreatitis.Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Oct;66(10):3597-3603. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06660-1. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Dig Dis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33094452
-
Diagnostic accuracy of interleukin-6 and procalcitonin in patients with periprosthetic joint infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Orthop. 2018 Jun;42(6):1213-1226. doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3744-3. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Int Orthop. 2018. PMID: 29294147
-
Laboratory markers predicting severity of acute pancreatitis.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2015;52(6):273-83. doi: 10.3109/10408363.2015.1051659. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2015. PMID: 26173077 Review.
Cited by
-
Heparin-binding Protein as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker of Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2025 May 1;17(1):e2025029. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2025.029. eCollection 2025. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40375914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of acute pancreatitis severity using NLR, procalcitonin, and CT severity score: A retrospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jul 4;104(27):e43055. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043055. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40629608 Free PMC article.
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol level as an independent protective factor against aggravation of acute pancreatitis: a case-control study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 6;14:1077267. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1077267. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38125797 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and Validation of a Nomogram Prediction Model for the Severe Acute Pancreatitis.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Jul 8;16:2831-2843. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S416411. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37449283 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-binding protein (HBP) worsens the severity of pancreatic necrosis via up-regulated M1 macrophages activation in acute pancreatitis mouse models.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):11978-11986. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2011018. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34895060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leppäniemi A, Tolonen M, Tarasconi A, et al. Executive summary: WSES Guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020;88(6):888‐890. - PubMed
-
- Schepers NJ, Bakker OJ, Besselink MG, et al. Impact of characteristics of organ failure and infected necrosis on mortality in necrotising pancreatitis. Gut. 2019;68(6):1044‐1051. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

