Role of the transcriptional regulator SP140 in resistance to bacterial infections via repression of type I interferons
- PMID: 34151776
- PMCID: PMC8248984
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.67290
Role of the transcriptional regulator SP140 in resistance to bacterial infections via repression of type I interferons
Abstract
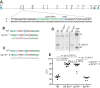
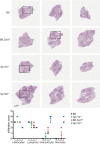
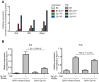
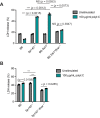
Type I interferons (IFNs) are essential for anti-viral immunity, but often impair protective immune responses during bacterial infections. An important question is how type I IFNs are strongly induced during viral infections, and yet are appropriately restrained during bacterial infections. The Super susceptibility to tuberculosis 1 (Sst1) locus in mice confers resistance to diverse bacterial infections. Here we provide evidence that Sp140 is a gene encoded within the Sst1 locus that represses type I IFN transcription during bacterial infections. We generated Sp140-/- mice and found that they are susceptible to infection by Legionella pneumophila and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Susceptibility of Sp140-/- mice to bacterial infection was rescued by crosses to mice lacking the type I IFN receptor (Ifnar-/-). Our results implicate Sp140 as an important negative regulator of type I IFNs that is essential for resistance to bacterial infections.
Keywords: immunology; inflammation; legionella pneumophila; mouse; mycobacterium tuberculosis; type i interferon.
© 2021, Ji et al.
Conflict of interest statement
DJ, KW, DK, SM, AL, VC, KC, MG, HD, AL, SN, DZ, IK, DP, KD No competing interests declared, RV consults for Ventus Therapeutics and is a Reviewing Editor for eLife
Figures





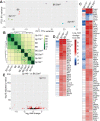
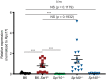


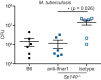
References
-
- Bhattacharya B, Xiao S, Chatterjee S, Urbanowski M, Ordonez A, Ihms EA, Agrahari G, Lun S, Berland R, Pichugin A, Gao Y, Connor J, Ivanov AR, Yan B-S, Kobzik L, Koo B-B, Jain S, Bishai W, Kramnik I. The integrated stress response mediates necrosis in murine Mycobacterium tuberculosis granulomas. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2021;131:e130319. doi: 10.1172/JCI130319. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

