How does the level of pulmonary venous isolation compare between pulsed field ablation and thermal energy ablation (radiofrequency, cryo, or laser)?
- PMID: 34151947
- PMCID: PMC8576283
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euab150
How does the level of pulmonary venous isolation compare between pulsed field ablation and thermal energy ablation (radiofrequency, cryo, or laser)?
Abstract
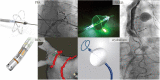
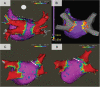
Aims: We studied the extent/area of electrical pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) after either pulsed field ablation (PFA) using a pentaspline catheter or thermal ablation technologies.
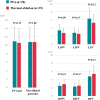
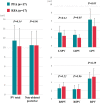
Methods and results: In a clinical trial (NCT03714178), paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF) patients underwent PVI with a multi-electrode pentaspline PFA catheter using a biphasic waveform, and after 75 days, detailed voltage maps were created during protocol-specified remapping studies. Comparative voltage mapping data were retrospectively collected from consecutive PAF patients who (i) underwent PVI using thermal energy, (ii) underwent reablation for recurrence, and (iii) had durably isolated PVs. The left and right PV antral isolation areas and non-ablated posterior wall were quantified. There were 20 patients with durable PVI in the PFA cohort, and 39 in the thermal ablation cohort [29 radiofrequency ablation (RFA), 6 cryoballoon, and 4 visually guided laser balloon]. Pulsed field ablation patients were younger with shorter follow-up. Left atrial diameter and ventricular systolic function were preserved in both cohorts. There was no significant difference between the PFA and thermal ablation cohorts in either the left- and right-sided PV isolation areas, or the non-ablated posterior wall area. The right superior PV isolation area was smaller with PFA than RFA, but this disappeared after propensity score matching. Notch-like normal voltage areas were seen at the posterior aspect of the carina in the balloon sub-cohort, but not the PFA or RFA cohorts.
Conclusion: Catheter-based PVI with the pentaspline PFA catheter creates chronic PV antral isolation areas as encompassing as thermal energy ablation.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Electroporation; Level of isolation; Pulmonary vein isolation; Pulsed field ablation.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


References
-
- Davalos RV, Mir LM, Rubinsky B.. Tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation. Ann Biomed Eng 2005;33:223–31. - PubMed
-
- Kotnik T, Kramar P, Pucihar G, Miklavčič D, Tarek M.. Cell membrane electroporation - Part 1: The phenomenon. IEEE Electr Insul Mag 2012;28:14–23.
-
- Reddy VY, Koruth J, Jais P, Petru J, Timko F, Skalsky I. et al. Ablation of atrial fibrillation with pulsed electric fields: an ultra-rapid, tissue-selective modality for cardiac ablation. JACC Clin Electrophysiol 2018;4:987–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

