Clinical and cost outcomes following genomics-informed treatment for advanced cancers
- PMID: 34152087
- PMCID: PMC8335838
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.4076
Clinical and cost outcomes following genomics-informed treatment for advanced cancers
Abstract
Background: Single-arm trials are common in precision oncology. Owing to the lack of randomized counterfactual, resultant data are not amenable to comparative outcomes analyses. Difference-in-difference (DID) methods present an opportunity to generate causal estimates of time-varying treatment outcomes. Using DID, our study estimates within-cohort effects of genomics-informed treatment versus standard care on clinical and cost outcomes.
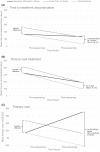
Methods: We focus on adults with advanced cancers enrolled in the single-arm BC Cancer Personalized OncoGenomics program between 2012 and 2017. All individuals had a minimum of 1-year follow up. Logistic regression explored baseline differences across patients who received a genomics-informed treatment versus a standard care treatment after genomic sequencing. DID estimated the incremental effects of genomics-informed treatment on time to treatment discontinuation (TTD), time to next treatment (TTNT), and costs. TTD and TTNT correlate with improved response and survival.
Results: Our study cohort included 346 patients, of whom 140 (40%) received genomics-informed treatment after sequencing and 206 (60%) received standard care treatment. No significant differences in baseline characteristics were detected across treatment groups. DID estimated that the incremental effect of genomics-informed versus standard care treatment was 102 days (95% CI: 35, 167) on TTD, 91 days (95% CI: -9, 175) on TTNT, and CAD$91,098 (95% CI: $46,848, $176,598) on costs. Effects were most pronounced in gastrointestinal cancer patients.
Conclusions: Genomics-informed treatment had a statistically significant effect on TTD compared to standard care treatment, but at increased treatment costs. Within-cohort evidence generated through this single-arm study informs the early-stage comparative effectiveness of precision oncology.
Keywords: biostatistics; genomic sequencing; healthcare costs; precision oncology; quasi-experimental methods; treatment outcomes.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Brandon Chan, Steven J.M. Jones, and Marco A. Marra report no conflicts of interest. Deirdre Weymann and Samantha Pollard codirect IMPRINT Research Consulting and have consulted for Roche Canada. Janessa Laskin has received honoraria for academic talks from: Roche Canada, Pfizer Canada, Astra‐Zeneca Canada, and BI Canada; her institution has received research funding for her projects from: Roche Canada, Asta‐Zeneca Canada, and BI Canada. Daniel J. Renouf disclosures include research funding and honoraria from Bayer and Roche, and travel funding and honoraria from Servier, Celgene, Taiho, Ipsen, and Astra Zenec. Howard Lim has received honoraria from Eisai, Taiho, Roche, Lilly, BMS, Amgen, and Leo for consultant work and is an investigator on trials with Bayer, BMS, Lilly, Roche, Astra‐Zeneca, and Amgen. Sophie Sun has received research grant and honoraria funding from Astra‐Zeneca. Stephen Yip is an advisory board member for and has received travel allowance from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Norvatis, and Roche. Dean A. Regier has received speaking honoraria from Roche Canada. DF Schaeffer has received honoraria from Alimentiv, Pfizer, Merck, and Diaceutics. Kasmintan A. Schrader has received speaking honoraria from AstraZeneca and Pfizer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Matching methods in precision oncology: An introduction and illustrative example.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021 Jan;9(1):e1554. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1554. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021. PMID: 33237632 Free PMC article.
-
A Retrospective Analysis of Precision Medicine Outcomes in Patients With Advanced Cancer Reveals Improved Progression-Free Survival Without Increased Health Care Costs.J Oncol Pract. 2017 Feb;13(2):e108-e119. doi: 10.1200/JOP.2016.011486. Epub 2016 Oct 31. J Oncol Pract. 2017. PMID: 27601506 Free PMC article.
-
Early-stage economic analysis of research-based comprehensive genomic sequencing for advanced cancer care.J Community Genet. 2022 Oct;13(5):523-538. doi: 10.1007/s12687-021-00557-w. Epub 2021 Nov 29. J Community Genet. 2022. PMID: 34843087 Free PMC article.
-
Translating genomics in cancer care.J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2013 Nov;11(11):1343-53. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2013.0158. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2013. PMID: 24225968 Review.
-
The future of cancer treatment using precision oncogenomics.Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2018 Apr 2;4(2):a002824. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a002824. Print 2018 Apr. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2018. PMID: 29610395 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative analysis of KRAS wildtype metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma reveals mutation and expression-based similarities to cholangiocarcinoma.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 8;13(1):5941. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33718-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36209277 Free PMC article.
-
Stakeholder Perspectives on Navigating Evidentiary and Decision Uncertainty in Precision Oncology.J Pers Med. 2022 Jan 1;12(1):22. doi: 10.3390/jpm12010022. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35055337 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of the differences in tumor mutation burden between primary and metastatic lesions by radiogenomics.Cancer Sci. 2022 Jan;113(1):229-239. doi: 10.1111/cas.15173. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Cancer Sci. 2022. PMID: 34689378 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating tumor DNA: toward evolving the clinical paradigm of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023 Mar 4;15:17588359231157651. doi: 10.1177/17588359231157651. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36895849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Building a Genomics-Informed Nursing Workforce: Recommendations for Oncology Nursing Practice and Beyond.Curr Oncol. 2024 Dec 27;32(1):14. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32010014. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39851930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weymann D, Pataky R, Regier DA. Economic evaluations of next‐generation precision oncology: a critical review. JCO Precis Oncol. 2018;2:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Le Tourneau C, Delord J‐P, Gonçalves A, et al. Molecularly targeted therapy based on tumour molecular profiling versus conventional therapy for advanced cancer (SHIVA): a multicentre, open‐label, proof‐of‐concept, randomised, controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1324–1334. - PubMed
-
- Tsimberidou AM, Kurzrock R. Precision medicine: lessons learned from the SHIVA trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:e579–e580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous