Non-C. difficile Clostridioides Bacteremia in Intensive Care Patients, France
- PMID: 34153220
- PMCID: PMC8237868
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2707.203471
Non-C. difficile Clostridioides Bacteremia in Intensive Care Patients, France
Abstract
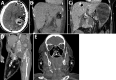
Usually responsible for soft tissue infections, Clostridioides species can also cause bacteremia, life-threatening infections often requiring intensive care unit (ICU) admission. We conducted a multicenter retrospective study to investigate Clostridioides bacteremia in ICUs to describe the clinical and biologic characteristics and outcomes in critically ill patients. We identified 135 patients with Clostridioides bacteremia, which occurred almost exclusively (96%) in patients with underlying conditions. Septic shock and digestive symptoms were the hallmarks of Clostridioides bacteremia in the ICU. We identified 16 different species of Clostridioides, among which C. perfringens accounted for 31% of cases. Despite the high sensitivity of Clostridioides to common antimicrobial drugs, mortality rates were high: 52% for ICU patients and 71% overall at 3 months. In multivariate analysis, the most important factor associated with increased risk for death was the presence of hemolysis. Clostridioides bacteremia often leads to multiple organ failures, which have high mortality rates.
Keywords: Clostridioides; Clostridium; France; ICU; bacteremia; bacteria; hemolysis; intensive care.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

