The Risk of Allergic Reaction to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines and Recommended Evaluation and Management: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, GRADE Assessment, and International Consensus Approach
- PMID: 34153517
- PMCID: PMC8248554
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaip.2021.06.006
The Risk of Allergic Reaction to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines and Recommended Evaluation and Management: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, GRADE Assessment, and International Consensus Approach
Abstract
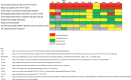
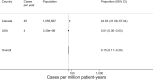
Concerns for anaphylaxis may hamper severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) immunization efforts. We convened a multidisciplinary group of international experts in anaphylaxis composed of allergy, infectious disease, emergency medicine, and front-line clinicians to systematically develop recommendations regarding SARS-CoV-2 vaccine immediate allergic reactions. Medline, EMBASE, Web of Science, the World Health Organizstion (WHO) global coronavirus database, and the gray literature (inception, March 19, 2021) were systematically searched. Paired reviewers independently selected studies addressing anaphylaxis after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polysorbate allergy, and accuracy of allergy testing for SARS-CoV-2 vaccine allergy. Random effects models synthesized the data to inform recommendations based on the Grading of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach, agreed upon using a modified Delphi panel. The incidence of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine anaphylaxis is 7.91 cases per million (n = 41,000,000 vaccinations; 95% confidence interval [95% CI] 4.02-15.59; 26 studies, moderate certainty), the incidence of 0.15 cases per million patient-years (95% CI 0.11-0.2), and the sensitivity for PEG skin testing is poor, although specificity is high (15 studies, very low certainty). We recommend vaccination over either no vaccination or performing SARS-CoV-2 vaccine/excipient screening allergy testing for individuals without history of a severe allergic reaction to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine/excipient, and a shared decision-making paradigm in consultation with an allergy specialist for individuals with a history of a severe allergic reaction to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine/excipient. We recommend further research to clarify SARS-CoV-2 vaccine/vaccine excipient testing utility in individuals potentially allergic to SARS-CoV2 vaccines or their excipients.
Keywords: Adenovirus-vector vaccine; Allergic reactions; Allergy; Allergy specialist; Anaphylaxis; COVID-19; GRADE; Polyethylene glycol; Polysorbate 80; SARS-CoV-2; Shared decision making; Skin testing; Vaccination; mRNA vaccine.
Copyright © 2021 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Recommendations were made for diagnosis and management of allergic reactions to COVID-19 vaccines.Ann Intern Med. 2021 Nov;174(11):JC122. doi: 10.7326/ACPJ202111160-122. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Ann Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 34724408
References
-
- Del Rio C., Malani P.N. COVID-19—new insights on a rapidly changing epidemic. JAMA. 2020;323:1339–1340. - PubMed
-
- Johns Hopkins University Coronavirus Resource Center. https://coronavirusjhuedu/maphtml Available from:
-
- Global Preparedness Monitoring Board . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2020. A World in Disorder. Global Preparedness Monitoring Board Annual Report 2020.https://apps.who.int/gpmb/assets/annual_report/GPMB_AR_2020_EN.pdf Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. Available from:
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Vaccines for COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/index.html Available from: - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

