Studies on the Regulation of Arginine Metabolism in Cyanobacteria Should Include Mixotrophic Conditions
- PMID: 34154397
- PMCID: PMC8262935
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01433-21
Studies on the Regulation of Arginine Metabolism in Cyanobacteria Should Include Mixotrophic Conditions
Keywords: arginine biosynthesis; arginine catabolism; mixotrophy; ornithine-ammonium cycle.
Figures
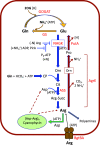
Comment on
-
The Novel PII-Interacting Protein PirA Controls Flux into the Cyanobacterial Ornithine-Ammonia Cycle.mBio. 2021 Mar 23;12(2):e00229-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00229-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33758091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herrero A, Flores E, Imperial J. 2019. Nitrogen assimilation in bacteria, p 280–300. In Schmidt TM (ed), Encyclopedia of microbiology, 4th ed, vol 3. Academic Press, Cambridge, MA.
-
- Flores E, Arévalo S, Burnat M. 2019. Cyanophycin and arginine metabolism in cyanobacteria. Algal Res 42:101577. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2019.101577. - DOI

