Role of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in the pathological mechanisms underlying maxillofacial cystic lesions
- PMID: 34155449
- PMCID: PMC8212445
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2021.1441
Role of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in the pathological mechanisms underlying maxillofacial cystic lesions
Abstract
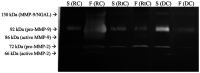
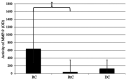
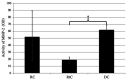
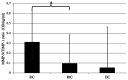
Cystic lesions are considered to be one of the most common pathologies of the maxillofacial region, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) may represent potential etiological factors. The aim of the present study was to elucidate the role of MMP-2 and MMP-9, and their endogenous tissue inhibitors, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 and TIMP-2, respectively, in the pathogenesis of maxillofacial cystic lesions. A total of 25 patients diagnosed with radicular cysts (RCs; n=20), dentigerous cysts (n=3) and retention cysts (RtCs; n=7) were enrolled in the present study. Gelatin zymography was performed to assess the gelatinolytic activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9, and commercial ELISA kits were used to determine TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 concentrations. Gelatin zymography revealed the presence of both MMP-2 and MMP-9 in all types of samples analyzed. An increase in MMP-9 activity, TIMP-1 concentration and MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio was observed in the fluid obtained from RCs compared with that obtained from RtCs. In conclusion, MMP-9 may be involved in the pathogenesis of RCs, whereas the activity of MMP-2 in the wall of RtCs was low, and this gelatinase did not appear to significantly affect the development of this type of lesion.
Keywords: dentigerous cyst; matrix metalloproteinase; matrixins; odontogenic cyst; radicular cyst; retentions cyst; tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase; zymography.
Copyright: © Kuźniarz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gene-expression analysis of matrix metalloproteinases 1 and 2 and their tissue inhibitors in chronic periapical inflammatory lesions.J Oral Pathol Med. 2016 Mar;45(3):224-30. doi: 10.1111/jop.12347. Epub 2015 Aug 21. J Oral Pathol Med. 2016. PMID: 26293377
-
Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and related tissue inhibitors in the cyst fluids of ovarian mucinous neoplasms.Gynecol Oncol. 2000 Aug;78(2):106-12. doi: 10.1006/gyno.2000.5856. Gynecol Oncol. 2000. PMID: 10926788
-
The expression and localization of selected matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, -7 and -9) and their tissue inhibitors (TIMP-2 and -3) in follicular cysts of sows.Theriogenology. 2022 Jun;185:109-120. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.03.029. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Theriogenology. 2022. PMID: 35395587
-
[Regulation of matrix-degrading enzymes in gynecologic cancer tissues and cells].Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996 Aug;48(8):618-22. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. PMID: 8808829 Japanese.
-
Altered balance between matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in experimental biliary fibrosis.Am J Pathol. 1998 Dec;153(6):1895-902. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65703-3. Am J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9846979 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Paradigm of the Inflammatory Radicular Cyst: Biological Aspects to be Considered.Eur Endod J. 2023 Jan;8(1):20-36. doi: 10.14744/eej.2022.26918. Eur Endod J. 2023. PMID: 36748442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine Profiling of Cyst Fluid and Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Cystic Vestibular Schwannoma.Otol Neurotol. 2023 Dec 1;44(10):1073-1081. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000004032. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Otol Neurotol. 2023. PMID: 37853737 Free PMC article.
-
Expression level and proteolytic activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in dental follicles, dentigerous cysts, odontogenic keratocysts and unicystic ameloblastomas.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2022 May-Jun;12(3):339-342. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2022.03.014. Epub 2022 Apr 6. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2022. PMID: 35433243 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Analysis of Genes Associated with the Pathogenesis of Odontogenic Keratocyst.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 17;25(4):2379. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042379. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38397053 Free PMC article.
-
IL-8 Is Upregulated in the Tissue-Derived EVs of Odontogenic Keratocysts.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 30;2022:9453270. doi: 10.1155/2022/9453270. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35941973 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
