Active transcutaneous bone-anchored hearing implant: how I do it
- PMID: 34155570
- PMCID: PMC8382654
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-021-06946-8
Active transcutaneous bone-anchored hearing implant: how I do it
Abstract
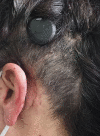
Background: The Cochlear™ Osia® System leaves a retroauricular bump that can cause discomfort and poor aesthetic outcome.
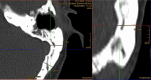
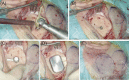
Method: To reduce the retroauricular bump, we introduced an implant well in the bone behind the ear for the transducer. We used cutting and diamond drills to create the implant well with an average depth of 4-5 mm. The surgical time including the implant well (40 min) was within the range of reported average surgical time (52 min).
Conclusion: Introduction of an implant well resulted in a better aesthetic outcome and improved patients' comfort. The reduced distance between BI300 and ear canal might improve audiological outcome.
Keywords: Auditory prosthesis; BAHI; Bone conduction hearing; Mixed hearing loss; OSIA; Single-sided deafness.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Arndt S—Cochlear Ltd., Lane Cove, Australia: research funding, reimbursement of travel expenses; MED-EL, Innsbruck, Österreich: research funding, reimbursement of travel expenses; Advanced Bionics, Stäfa, Schweiz: research funding, reimbursement of travel expenses; Oticon Medical A/S, Smørum, Dänemark: research funding, reimbursement of travel expenses. Rauch AK—MED-EL, Innsbruck, Österreich: reimbursement of travel expenses. Speck I—Cochlear Ltd., Lane Cove, Australia: reimbursement of travel expenses.
Figures



References
-
- Osia 2 System Datasheet (2021) D1618102. Cochlear Bone Anchored Solutions AB, Sweden
-
- Goldstein MR, Bourn S, Jacob A. Early Osia® 2 bone conduction hearing implant experience: nationwide controlled-market release data and single-center outcomes. Am J Otolaryngol Head Neck Med Surg. 2021;42:102818. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

