HepCCATT: a multilevel intervention for hepatitis C among vulnerable populations in Chicago
- PMID: 34156077
- PMCID: PMC8692481
- DOI: 10.1093/pubmed/fdab190
HepCCATT: a multilevel intervention for hepatitis C among vulnerable populations in Chicago
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis C infection could be eliminated. Underdiagnosis and lack of treatment are the barriers to cure, especially for vulnerable populations (i.e. unable to pay for health care).
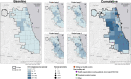
Methods: A multilevel intervention from September 2014 to September 2019 focused on the providers and organizations in 'the safety net' (providing health care to populations unable to pay), including: (i) public education, (ii) training for primary care providers (PCPs) and case managers, (iii) case management for high-risk populations, (iv) policy advice and (v) a registry (Registry) for 13 health centers contributing data. The project tracked the number of PCPs trained and, among Registry sites, the number of people screened, engaged in care (i.e. clinical follow-up after diagnosis), treated and/or cured.
Results: In Chicago, 215 prescribing PCPs and 56 other health professionals, 86% of whom work in the safety net, were trained to manage hepatitis C. Among Registry sites, there was a 137% increase in antibody screening and a 32% increase in current hepatitis C diagnoses. Engagement in care rose by 18%.
Conclusions: Hepatitis C Community Alliance to Test and Treat (HepCCATT) successfully targeted safety net providers and organizations with a comprehensive care approach. While there were challenges, HepCCATT observed increased hepatitis C screening, diagnosis and engagement in care in the Chicago community.
Keywords: disease registries; health services; liver disorders.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Faculty of Public Health. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hoofnagle JH. Course and outcome of hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002 Nov;36(5 Suppl 1):S21–9. - PubMed
-
- Rustgi VK. The epidemiology of hepatitis C infection in the United States. J Gastroenterol 2007 Jul;42(7):513–21. - PubMed
-
- Recommendations for prevention and control of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and HCV-related chronic disease. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. MMWR Recomm Rep 1998 Oct 16;47(RR-19):1–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

